Nutrition in CrossFit® - scientific evidence and practical perspectives: a systematic scoping review
- PMID: 40471841
- PMCID: PMC12143013
- DOI: 10.1080/15502783.2025.2509674
Nutrition in CrossFit® - scientific evidence and practical perspectives: a systematic scoping review
Abstract
Background: CrossFitⓇ sessions and competitions are characterized by high-intensity challenges that combine aerobic and anaerobic activities with short recovery periods. As a result, effective nutritional practices play a crucial role in optimizing performance and enhancing recovery. Therefore, nutritional practices are central to optimizing performance and accelerating recovery. This review aims to summarize current evidence on nutritional and ergogenic aid responses to CrossFitⓇ practice.
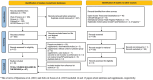
Methods: The search was conducted in four electronic databases (PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus and SportDiscus). Gray literature was also extracted for studies exploring the nutritional habits of CrossFitⓇ participants as well as the ingestion of ergogenic aids. In addition, a meta-analysis was conducted to examine the impacts of dietary habits and ergogenic aids on performance.
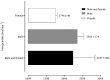
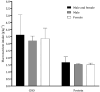
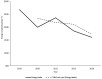
Results: Forty-nine studies met the eligibility criteria and were included in the current review. Carbohydrate intake was below the recommendations for athletes, although protein ingestion remains adequate. High-carbohydrate diets had a positive effect on CrossFitⓇ performance. The evidence concerning the effects of a ketogenic diet on performance is limited. When used prior to or during the workout, the impact of carbohydrates on CrossFitⓇ performance was negligible, whereas the effect of caffeine was significant. Ergogenic aids, particularly creatine and protein, are commonly used by CrossFitⓇ participants.
Conclusion: The standard diets recommended to CrossFitⓇ participants need to be revised because they are characterized by lower values of carbohydrates. Caffeine should be used prior to or during the CrossFitⓇ sessions. Regarding the impact of ergogenic aids on recovery, future studies are needed.
Keywords: Carbohydrates; caffeine; conditioning; energy; performance; strength.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
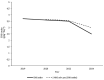
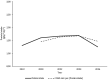




References
-
- CrossFit® Growth Statistics: Global Reach, Revenue and Participation Soar . https://worldmetrics.org/crossfit-growth-statistics/consulted2024
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
