Development and validation of a measurement instrument for student assessment of quality physical education in Chinese secondary schools
- PMID: 40471878
- PMCID: PMC12140257
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324227
Development and validation of a measurement instrument for student assessment of quality physical education in Chinese secondary schools
Abstract
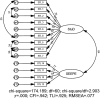
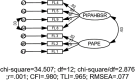
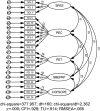
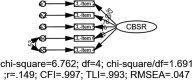
There is a growing emphasis on developing Quality Physical Education (QPE) programs. However, a research gap exists due to the lack of measurement instruments to assess QPE for students. This study aimed to develop an instrument to assess QPE implementation and its validity and reliability in China. This study comprised three phases. In Phase 1, a conceptual framework for QPE was established using grounded theory based on interviews with 22 PE teachers and 20 students. In Phase 2, using the conceptual framework from Phase 1, we developed an item pool supported by a literature review, expert evaluations, and student interviews. In Phase 3, a cross-sectional study was conducted with secondary school students (705 participants) to analyse the items and assess the instrument's reliability and validity through exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis, as well as test-retest analysis. The final 45-item instrument, comprising four subscales (student, family, school, and community) across 10 factors, demonstrated strong validity and reliability. Model fit indices met established thresholds (e.g., CFI and TLI ≥ .90, as well as RMSEA ≤ .08). The composite reliability and average variance extracted values for each factor exceeded.7 and.5, respectively, with the test-retest reliability also exceeding.7, indicating high reliability and validity. This study addresses a critical methodological gap in QPE research by developing a culturally contextualized assessment instrument that explicitly identifies and measures students' perceptions of QPE implementation. This instrument enables systematic monitoring of QPE practices from students' perspectives, informing evidence-based policymaking and resource allocation. Integrating student, family, school, and community subscales supports holistic interventions to improve the quality of PE.
Copyright: © 2025 Qin et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Developing a model of quality physical education in the Chinese context: a grounded theory investigation of secondary school physical education teachers' perceptions.Front Public Health. 2025 May 1;13:1569222. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1569222. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40385620 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the achievement emotions questionnaire for physical education in university students.BMC Public Health. 2023 Sep 21;23(1):1839. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16759-5. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37735395 Free PMC article.
-
Development and psychometric testing of the Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices (KAP) questionnaire among student Tuberculosis (TB) Patients (STBP-KAPQ) in China.BMC Infect Dis. 2018 May 8;18(1):213. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3122-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29739363 Free PMC article.
-
Psychometric properties of the Chinese version physical literacy assessment questionnaire among high school students in Gansu, China.PeerJ. 2025 Apr 9;13:e19093. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19093. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40226541 Free PMC article.
-
[Psychometric characteristics of questionnaires designed to assess the knowledge, perceptions and practices of health care professionals with regards to alcoholic patients].Encephale. 2004 Sep-Oct;30(5):437-46. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(04)95458-9. Encephale. 2004. PMID: 15627048 Review. French.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global status report on physical activity 2022. 2022. Available from: https://www.who.int/teams/health-promotion/physical-activity/global-stat...
-
- Huo M, Yang Z. Exercise, Depression, and Anxiety in Young People: A Cross-Sectional Survey. International Journal of Mental Health Promotion. 2023;25(4):551–62. doi: 10.32604/ijmhp.2023.023406 - DOI
-
- Li W, Xiang P. A Review on the Dose Response Effect of Regular Physical Activity on Cognitive Function Among Children and Adolescents. IJPAH. 2023. doi: 10.18122/ijpah.020203.boisestate - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

