Modelling of ankle joint range of motion and landing quality scores in female soccer players with quantile regression approach
- PMID: 40472041
- PMCID: PMC12140249
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325180
Modelling of ankle joint range of motion and landing quality scores in female soccer players with quantile regression approach
Abstract
Purpose: Ankle dorsiflexion range of motion (DF-ROM) has been shown to be associated with poor landing posture. This study aimed to model the relationship between DF-ROM and landing quality during the Soccer-Specific Jump-Landing task (SSJL) on the non-dominant extremity in elite and amateur female soccer players using a quantile regression approach.
Methods: 55 amateur and 47 professional female soccer players participated in the study. The relationship between DF-ROM and SSJL quality was evaluated using Pearson's product-moment correlation analysis and Quantile regression modelling.
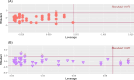
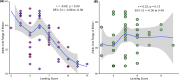
Results: There was a statistically significant negative correlation between DF-ROM and SSJL landing quality among female soccer players (r = - 0.33, p = 0.001). Moreover, there was a statistically significant negative correlation between DF-ROM and SSJL landing quality in amateur female soccer players (r = - 0.63, p = 0.001), no significant correlation was found in elite female soccer players (r = 0.22, p = 0.13). Quantile regression results for amateur female soccer players indicate that the association between ankle DF-ROM and landing quality is stronger in athletes with higher SSJL landing quality scores (e.g., Q75 and Q90) compared to those with lower scores (e.g., Q10 and Q25). This suggests that ankle DF-ROM plays a more critical role in achieving higher-quality landing techniques than in poorer techniques.
Conclusions: Higher quality landing techniques in female soccer players are associated with larger ranges of ankle DF-ROM. Therefore, ankle DF-ROM level may be a functional clinical measurement for amateur female athletes in determining landing-related injury risk factors during SSJL.
Copyright: © 2025 Rad et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

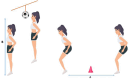
References
-
- Hosseini K, Mohammadian Z, Alimoradi M, Shabani M, Armstrong R, Hogg J, et al. The immediate effect of a balance wobble board protocol on knee and ankle joint position sense in female soccer players. Acta Gymnica. 2023;53. doi: 10.5507/ag.2023.011 - DOI
-
- ROSSO E. From Informal Recreation to a Geography of Achievement: Women’s Soccer in South Australia. Geographical Research. 2010;48(2):181–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-5871.2009.00618.x - DOI
-
- Martín-San Agustín R, Medina-Mirapeix F, Esteban-Catalán A, Escriche-Escuder A, Sánchez-Barbadora M, Benítez-Martínez JC, et al. Epidemiology of Injuries in First Division Spanish Women’s Soccer Players. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(6):3009. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18063009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

