Serum Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker for CIDP Diagnosis, Severity, and Treatment Outcome
- PMID: 40472292
- PMCID: PMC12153944
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200419
Serum Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker for CIDP Diagnosis, Severity, and Treatment Outcome
Abstract
Background and objectives: The aim of this study was to characterize serum neurofilament light chain (sNFL) levels in a large cohort of patients with autoimmune neuropathies to provide every-day clinical practice recommendations.
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, we recruited 191 patients with immune-mediated neuropathies from 2 referral centers. sNFL was measured using the Simoa NF-light kit (Quanterix), and age-corrected and BMI-corrected z-scores (zNFL) were calculated. Clinical data were correlated with zNFL and adjusted for different disease subsets. A receiver operator characteristic analysis was performed. Treatments and longitudinal disease course of patients with typical chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) in early disease stage were analyzed.
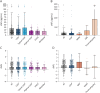
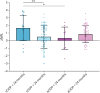
Results: One hundred ten patients had typical CIDP, and 67 had atypical CIDP. Fourteen patients had other immune neuropathies. zNFL of all patients correlated significantly with the Inflammatory Neuropathy Cause and Treatment Scale-overall disability sum score (r = 0.160), Medical Research Council Scale for Muscle Strength score (r = -0.242), modified Rankin Scale score (r = 0.151), and distal tibial compound muscle action potential (r = -0.151). The correlations remained only in the cohort of typical CIDP. zNFL >2 within the first 24 months of illness differentiated patients with atypical and typical CIDP with a sensitivity of 93%. Patients with early-stage typical CIDP with zNFL >2 (n = 9) presented with the most severe manifestation and did not respond to first-line (p < 0.0001) but to second-line treatments.
Discussion: We established sNFL as a promising biomarker for assessing disease activity in patients with typical CIDP. Elevated zNFL in early-stage typical CIDP indicate severe inflammatory-mediated axonal damage that requires aggressive immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no relevant disclosures. Go to
Figures


Similar articles
-
Treatments for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP): an overview of systematic reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 13;1(1):CD010369. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010369.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28084646 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory treatment other than corticosteroids, immunoglobulin and plasma exchange for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 8;5(5):CD003280. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003280.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28481421 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Corticosteroids for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 29;11(11):CD002062. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002062.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29185258 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous immunoglobulin for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(2):CD001797. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001797. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Jan 21;(1):CD001797. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001797.pub2. PMID: 12076423 Updated.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
