Mutations in the floral regulator gene HUA2 restore flowering to the Arabidopsis trehalose 6-phosphate synthase1 (tps1) mutant
- PMID: 40472318
- PMCID: PMC12198769
- DOI: 10.1093/plphys/kiaf225
Mutations in the floral regulator gene HUA2 restore flowering to the Arabidopsis trehalose 6-phosphate synthase1 (tps1) mutant
Abstract
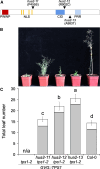
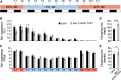
Plant growth and development are regulated by many factors, including carbohydrate availability and signaling. Trehalose 6-phosphate (T6P), which is synthesized by TREHALOSE-6-PHOSPHATE SYNTHASE 1 (TPS1), is positively associated with and functions as a signal that informs the cell about the carbohydrate status. Mutations in TPS1 negatively affect the growth and development of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), and complete loss-of-function alleles are embryo-lethal, which can be overcome using inducible expression of TPS1 (GVG::TPS1) during embryogenesis. Using ethyl methane sulfonate mutagenesis in combination with genome re-sequencing, we have identified several alleles in the floral regulator gene HUA2 that restore flowering in tps1-2 GVG::TPS1. Genetic analyses using an HUA2 T-DNA insertion allele, hua2-4, confirmed this finding. RNA-seq analyses demonstrated that hua2-4 has widespread effects on the tps1-2 GVG::TPS1 transcriptome, including key genes and pathways involved in regulating flowering. Higher order mutants combining tps1-2 GVG::TPS1 and hua2-4 with alleles in the key flowering time regulators FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT), SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CONSTANS 1 (SOC1), and FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC) were constructed to analyze the role of HUA2 during floral transition in tps1-2 in more detail. Our findings demonstrate that loss of HUA2 can restore flowering in tps1-2 GVG::TPS1, in part through activation of FT, with contributions from the upstream regulators SOC1 and FLC. Interestingly, we found that mutation of FLC is sufficient to induce flowering in tps1-2 GVG::TPS1. Furthermore, we observed that mutations in HUA2 modulate carbohydrate signaling and that this regulation might contribute to flowering in hua2-4 tps1-2 GVG::TPS1.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Society of Plant Biologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement. None declared.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The trehalose 6-phosphate pathway coordinates dynamic changes at the shoot apical meristem in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Physiol. 2025 Sep 1;199(1):kiaf300. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiaf300. Plant Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40638795 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the PWWP-domain protein HUA2 and the H3K36 methylation in flowering time control.Plant J. 2025 Sep;123(5):e70461. doi: 10.1111/tpj.70461. Plant J. 2025. PMID: 40913804
-
Integrated expression analysis to elucidate the role of miR394 during flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell Rep. 2025 Jul 2;44(7):167. doi: 10.1007/s00299-025-03541-7. Plant Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40601081
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

