Knowledge about head and neck cancer among adolescents
- PMID: 40472627
- PMCID: PMC12171557
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2025.101608
Knowledge about head and neck cancer among adolescents
Abstract
Objective: To assess knowledge about head and neck cancer among adolescents from private schools, aged between 13 and22 years.
Methods: 200 questionnaires were applied among students, about the profile of adolescents and their knowledge about head and neck neoplasms, treatment, and teaching in schools on this topic. The results were analyzed both quantitatively and qualitatively.
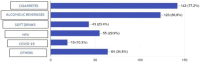
Results: Only 55 students (29.9%) identified HPV as a risk factor for the disease. 137 students (74.5%) identified the brain as an organ treated by head and neck surgery. As for the therapeutic strategies used for the treatment of neoplasms in the region, only 67 students (36.4%) are aware. On the topic of teaching in schools, 153 students (83.1%) relate to some deficiency in the approach and learning.
Conclusion: Knowledge about head and neck cancer is insufficient. It is necessary to introduce in the curriculum basic cancer education in biology classes. The expansion of acquirements about cancer can provide better care and the ability to identify risk factors, initial signs, and symptoms of the disease, as well as the incorporation of healthy habits in families because these students can propagate valid information in their environment.
Level of evidence: Level IV.
Keywords: Adolescent behavior; Head and neck neoplasms; Health knowledge.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier España S.L.U.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sawyer S.M., Azzopardi P.S., Wickremarathne D., Patton G.C. The age of adolescence. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2018;2:223–228. - PubMed
-
- Clarke B. The angst, anguish and ambitions of the teenage years. Young Consum. 2003;4:27–33.
-
- Brêtas J.R.S., Moreno R.S., Eugenio D.S., Sala D.C.P., Vieira T.F., Bruno P.R. Passage rituals according to adolescents. Acta Paul Enferm. 2008;21:404–411.
-
- Brasil. Ministério da Educação. (2018). Português tem apenas 1,6% de aprendizagem adequada no Saeb [Internet]. [cited 2020 Nov 12]. Available from: http://portal.mec.gov.br/ultimas-noticias/389-ensinomedio2092297298/6827....
-
- Gilz C., Scortegagna A. In: Anais do XI Congresso Nacional de Educação; 2013. PUCPR; Curitiba: 2013. A percepção do aluno do ensino médio em relação às dificuldades de aprendizagem; pp. 5643–5656.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials