ADAMTS5 Modulates Breast Cancer Development as a Diagnostic Biomarker and Potential Tumour Suppressor, Regulated by BAIAP2-AS1, CRNDE and hsa-miR-135b-3p: Integrated Systems Biology and Experimental Approach
- PMID: 40472834
- PMCID: PMC12140660
- DOI: 10.1049/syb2.70015
ADAMTS5 Modulates Breast Cancer Development as a Diagnostic Biomarker and Potential Tumour Suppressor, Regulated by BAIAP2-AS1, CRNDE and hsa-miR-135b-3p: Integrated Systems Biology and Experimental Approach
Abstract
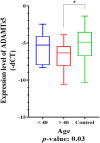
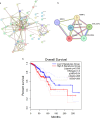
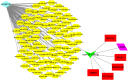
ADAMTS5, a member of the ADAMTS family, exhibits crucial biological roles, including protein shedding, proteolysis, and cell migration. Its relevance in breast cancer (BC) was explored through an integrative approach combining high-throughput analyses, database validations, and experimental confirmation. ADAMTS5 expression was significantly reduced in BC samples, as verified by microarray analysis, qRT-PCR, and public database resources. A protein-protein interaction network revealed five proteins-COL10A1, COL11A1, COMP, MMP1 and SDC1-that interact with ADAMTS5 and are primarily associated with the ECM-receptor interaction pathway. These proteins also engage in cell cycle checkpoint signalling, emphasising their potential role in tumour progression. Survival analysis of BC samples identified a novel prognostic signature based on ADAMTS5-related proteins. The study extended to coding and noncoding RNA interactions, identifying lncRNAs as key regulators. CRNDE acts as a ceRNA for ADAMTS5, modulating its expression via hsa-miR-135b-3p. Meanwhile, BAIAP2-AS1 interacts directly with ADAMTS5, offering another layer of regulatory control and prognostic value. These findings position ADAMTS5 as a vital player in BC biology, with its low expression linked to critical pathways and survival outcomes. The identified lncRNA-mediated regulatory mechanisms add depth to understanding ADAMTS5's role and suggest potential targets for therapeutic development. This study underscores ADAMTS5's potential as a biomarker and its broader implications in unravelling BC molecular mechanisms.
Keywords: bioinformatics; cancer genomics; computational biology; gene regulatory network; prognostic biomarker.
© 2025 The Author(s). IET Systems Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Institution of Engineering and Technology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Kobayashi H., Hirata M., Saito T., Itoh S., Chung U. I., and Kawaguchi H., “Transcriptional Induction of ADAMTS5 Protein by Nuclear Factor‐κB (NF‐κB) Family Member RelA/p65 in Chondrocytes During Osteoarthritis Development,” Journal of Biological Chemistry 288, no. 40 (October 2013): 28620–28629, 10.1074/jbc.m113.452169. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

