Imaging Efficacy of [18F]CTT1057 PET for the Detection of PSMA-Positive Tumors Using Histopathology as Standard of Truth: Results from the GuideView Phase 2/3 Prospective Multicenter Study
- PMID: 40473463
- PMCID: PMC12320564
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.124.269007
Imaging Efficacy of [18F]CTT1057 PET for the Detection of PSMA-Positive Tumors Using Histopathology as Standard of Truth: Results from the GuideView Phase 2/3 Prospective Multicenter Study
Abstract
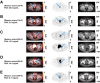
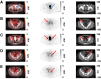
[18F]CTT1057 is a highly selective prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-targeted PET radiotracer for prostate cancer (PCa) detection. This prospective study (GuideView, NCT04838626) evaluates the imaging efficacy of [18F]CTT1057 PET to detect PSMA-positive lesions against histopathology in patients with newly diagnosed, untreated, high-risk PCa. Methods: Between September 7, 2021, and October 26, 2023, 201 patients planned for radical prostatectomy were screened and 195 patients were enrolled. Of these, 184 patients received a median of 355 MBq (range, 195-400 MBq) of [18F]CTT1057 and underwent PET/CT 90 min (±30 min) later. Three masked central independent readers evaluated the images. Coprimary endpoints were patient-level sensitivity (including primary tumor and pelvic lymph nodes) and region-level specificity (including pelvic lymph nodes only) for detection of PSMA-positive lesions, using histopathology as the standard of truth. The lower-bound 95% CI needed to surpass 50% for patient-level sensitivity and 70% for region-level specificity. Success was defined as at least 2 of 3 central readers meeting these criteria. Secondary endpoints included the patient-level and region-level positive predictive value and accuracy, region-level sensitivity, inter- and intrareader variability, detection rate of distant metastasis, pharmacokinetics, and safety and tolerability assessments. Results: Of the 184 patients who received [18F]CTT1057, 172 patients were evaluable for efficacy. Among these, a median of 19 lymph nodes (interquartile range, 13.0-28.5 lymph nodes) were dissected per patient. Both coprimary endpoints were met, with lower bounds of 95% CIs surpassing the success criteria for all 3 readers for both patient-level sensitivity (range, 86.8%-90.0%; lower-bound 95% CI, 80.7%-84.5%) and region-level specificity (97.1%; lower-bound 95% CI, 92.7%). Interreader variability Fleiss κ was 63.9%; intrareader reproducibility Cohen κ was 89.4%-100%. [18F]CTT1057 had a favorable safety profile. Conclusion: GuideView confirmed the imaging efficacy of [18F]CTT1057 for the detection of PSMA-positive lesions, with high patient-level sensitivity and region-level specificity. Substantial interreader variability and almost perfect intrareader reproducibility suggest that [18F]CTT1057 findings are robust and reliable. [18F]CTT1057 will contribute to expanding access to PSMA PET imaging to properly diagnose and treat patients with PCa.
Keywords: PET; [18F]CTT1057; high-risk prostate cancer; molecular imaging; prostate-specific membrane antigen.
© 2025 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Imaging Efficacy of [18F]CTT1057 PET/CT in Patients with Biochemically Recurrent Prostate Cancer: Results from GuidePath-A Phase 3, Prospective Multicenter Study.J Nucl Med. 2025 Aug 1;66(8):1210-1216. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.124.269266. J Nucl Med. 2025. PMID: 40473464 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Can Negative Prostate-specific Membrane Antigen Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography Avoid the Need for Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection in Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer Patients? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis with Backup Histology as Reference Standard.Eur Urol Oncol. 2022 Feb;5(1):1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2021.08.001. Epub 2021 Sep 17. Eur Urol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34538770
-
A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of the Role of Prostate-specific Membrane Antigen Positron Emission Tomography for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis and Primary Staging before Definitive Treatment.Eur Urol. 2025 Jun;87(6):654-671. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2025.03.003. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Eur Urol. 2025. PMID: 40155242
-
Multicenter External Validation and Optimization of a Proposed Nomogram for Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen PET/CT Accuracy in Biochemical Recurrence.Prostate. 2025 Aug;85(11):1016-1023. doi: 10.1002/pros.24910. Epub 2025 May 6. Prostate. 2025. PMID: 40329523
-
PSMA-PET-derived distance features as biomarkers for predicting outcomes in primary prostate cancer post-radical prostatectomy.Cancer Imaging. 2025 Jul 22;25(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s40644-025-00907-8. Cancer Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40696478 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Imaging Efficacy of [18F]CTT1057 PET/CT in Patients with Biochemically Recurrent Prostate Cancer: Results from GuidePath-A Phase 3, Prospective Multicenter Study.J Nucl Med. 2025 Aug 1;66(8):1210-1216. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.124.269266. J Nucl Med. 2025. PMID: 40473464 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Cornford P, van den Bergh RCN, Briers E, et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-ISUP-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer: 2024 update. Part I: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent. Eur Urol. 2024;86:148–163. - PubMed
-
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines) for Prostate Cancer V.2.2025. National Comprehensive Cancer Network website. https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail?id=1459. Accessed May 27, 2025.
-
- Drug approval package: gallium Ga 68 PSMA-11. Food and Drug Administration website. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2020/212642Orig1s000T.... Published December 1, 2020. Accessed March 5, 2025.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
