Microbiota-derived butyrate alleviates asthma via inhibiting Tfh13-mediated IgE production
- PMID: 40473603
- PMCID: PMC12141656
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-025-02263-2
Microbiota-derived butyrate alleviates asthma via inhibiting Tfh13-mediated IgE production
Abstract
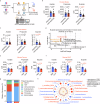
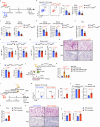
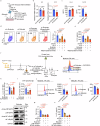
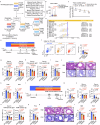
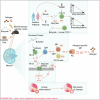
Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) impact asthma outcomes, highlighting the importance of understanding the disease mechanisms through the gut-lung axis. In this study, we identified that among SCFAs, butyrate uniquely alleviates asthma through specifically inhibiting a newly identified pathogenic T follicular helper (Tfh) cell subset, Tfh13 cells. Tfh13 cell depletion (Il13Cre/+Bcl6fl/fl) or adoptive transfer of Tfh13 cells in an OVA-induced asthma model conclusively demonstrated their indispensable role in driving anaphylactic IgE production and asthma pathogenesis. Mechanistically, the inhibitory function of butyrate on Tfh13 cells is mediated by the interaction between butyrate and G-protein coupled receptor 43 (GPR43), leading to the suppression of p38 MAPK/NF-κB signaling in Tfh13 cells. To address the clinically observed deficiency of butyrate in patients with asthma and recapitulated in murine models, we developed a novel therapeutic strategy using a butyrate-yielding diet enriched with butylated high amylose maize starch (HAMSB). Remarkably, supplementation with HAMSB diet in murine and humanized asthma models significantly reduced Tfh13 cell frequencies and anaphylactic IgE levels, leading to significantly improved disease outcomes. Our findings not only unveil a novel mechanism underlying butyrate-mediated asthma alleviation, termed the butyrate-Tfh13-IgE axis, but also propose a clinically translatable dietary intervention strategy targeting microbial metabolites for stopping asthma.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Lynch, S. V. & Pedersen, O. The human intestinal microbiome in health and disease. N. Engl. J. Med.375, 2369–2379 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Pabst, O. et al. Gut-liver axis: barriers and functional circuits. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.20, 447–461 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Glorieux, G., Nigam, S. K., Vanholder, R. & Verbeke, F. Role of the microbiome in gut-heart-kidney cross talk. Circ. Res.132, 1064–1083 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Fan, S. et al. Microbiota-gut-brain axis drives overeating disorders. Cell Metab.35, 2011–2027.e2017 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82121002/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82130050/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82330053/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81971493/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

