Characterization of a suspension Vero cell line for viral vaccine production
- PMID: 40473628
- PMCID: PMC12141672
- DOI: 10.1038/s41541-025-01157-2
Characterization of a suspension Vero cell line for viral vaccine production
Abstract
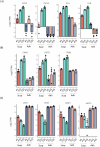
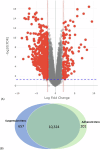
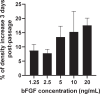
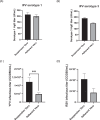
Vero cells, as approved by the World Health Organization, have been the most commonly used continuous cell line for viral vaccine production over the last 25 years, but their adherent phenotype continues to limit productivity. Adapting to a suspension culture would overcome this restriction and reduce production costs. First, a Vero suspension isolate was obtained and metabolically characterized. Second, RNA sequencing analysis was used to identify differentially expressed genes between adherent and suspension cells, which revealed complete downregulation of adhesion and matrix-associated genes. Additionally, signaling pathways involving Wnt and other tyrosine kinase receptors were identified as potential leads for growth optimization. In particular, supplementation with fibroblast growth factor 2 allowed for a 20% increase in cell density. Finally, a comparative viral productivity assay revealed a 30% increase in poliovirus production in suspension Vero cells compared to adherent cells depending on the serotype, as well as a 140% increase in respiratory syncytial virus production and a 150% increase in yellow fever virus production. This work establishes the potential of the suspension Vero cell line as a new cell platform for viral vaccine production.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare the following financial interests and personal relationships as potential competing interests: This work was funded by Sanofi. Léa Bourigault, Corinne Bresson, Christophe Chevalard, Damien Soulet, Fleurine Pelissier, Stéphanie Richard, Isabelle Bassard, Nicolas Sève, and Cédric Charretier are Sanofi employees and may hold shares or stocks in the company.
Figures
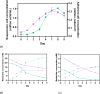
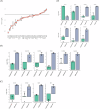
 ) and lactate measured in the supernatant (
) and lactate measured in the supernatant ( ), C concentrations of glutamine (
), C concentrations of glutamine ( ) and ammonium ions (
) and ammonium ions ( ) measured in the supernatant. The error bars represent the standard deviation for N = 3 distinct cultures for each condition.
) measured in the supernatant. The error bars represent the standard deviation for N = 3 distinct cultures for each condition.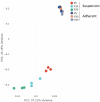
References
-
- Meeting, W.E.C.o.B.S. & Standardization, W.H.O.E.C.o.B. WHO Expert Committee on Biological Standardization: Sixty-first Report, Vol. 978. (World Health Organization, 2013).
-
- Yasumura, Y. & Kawakita, Y. Studies on SV40 in tissue culture-preliminary step for cancer research in vitro. Nihon Rinsho21, 1201–1215 (1963).
-
- Vlecken, D. H., Pelgrim, R. P., Ruminski, S., Bakker, W. A. & van der Pol, L. A. Comparison of initial feasibility of host cell lines for viral vaccine production. J. Virol. Methods193, 28–41 (2013). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

