GNNs surpass transformers in tumor medical image segmentation
- PMID: 40473649
- PMCID: PMC12141428
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-00002-9
GNNs surpass transformers in tumor medical image segmentation
Abstract
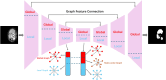
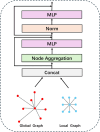
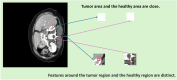
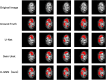
To assess the suitability of Transformer-based architectures for medical image segmentation and investigate the potential advantages of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) in this domain. We analyze the limitations of the Transformer, which models medical images as sequences of image patches, limiting its flexibility in capturing complex and irregular tumor structures. To address it, we propose U-GNN, a pure GNN-based U-shaped architecture designed for medical image segmentation. U-GNN retains the U-Net-inspired inductive bias while leveraging GNNs' topological modeling capabilities. The architecture consists of Vision GNN blocks stacked into a U-shaped structure. Additionally, we introduce the concept of multi-order similarity and propose a zero-computation-cost approach to incorporate higher-order similarity in graph construction. Each Vision GNN block segments the image into patch nodes, constructs multi-order similarity graphs, and aggregates node features via multi-order node information aggregation. Experimental evaluations on multi-organ and cardiac segmentation datasets demonstrate that U-GNN significantly outperforms existing CNN- and Transformer-based models. U-GNN achieves a 6% improvement in Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) and an 18% reduction in Hausdorff Distance (HD) compared to state-of-the-art methods. The source code will be released upon paper acceptance.
Keywords: CNN; GNN; Medical image segmentation; Transformer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no interest/Competing interests. Ethical approval and consent to participate: All data used in this study are sourced from publicly available datasets. Since the research does not compromise personal interests, involve sensitive information, or have commercial implications, it is exempt from ethical review.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multi-scale graph harmonies: Unleashing U-Net's potential for medical image segmentation through contrastive learning.Neural Netw. 2025 Feb;182:106914. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2024.106914. Epub 2024 Nov 23. Neural Netw. 2025. PMID: 39608151
-
Dual encoder network with transformer-CNN for multi-organ segmentation.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2023 Mar;61(3):661-671. doi: 10.1007/s11517-022-02723-9. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2023. PMID: 36580181
-
TransUNet: Rethinking the U-Net architecture design for medical image segmentation through the lens of transformers.Med Image Anal. 2024 Oct;97:103280. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2024.103280. Epub 2024 Jul 22. Med Image Anal. 2024. PMID: 39096845
-
Efficient brain tumor segmentation using Swin transformer and enhanced local self-attention.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2024 Feb;19(2):273-281. doi: 10.1007/s11548-023-03024-8. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2024. PMID: 37796413 Review.
-
Advantages of transformer and its application for medical image segmentation: a survey.Biomed Eng Online. 2024 Feb 3;23(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12938-024-01212-4. Biomed Eng Online. 2024. PMID: 38310297 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sun, D.-Y. et al. Unlocking the full potential of memory t cells in adoptive t cell therapy for hematologic malignancies. Int. Immunopharmacol.144, 113392 (2025). - PubMed
-
- Wang, S. et al. Discovery of a highly efficient nitroaryl group for detection of nitroreductase and imaging of hypoxic tumor cells. Organ. Biomol. Chem.19(15), 3469–3478 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

