Assessing individual head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patient response to therapy through integration of functional and genomic data
- PMID: 40473660
- PMCID: PMC12141454
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-03111-7
Assessing individual head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patient response to therapy through integration of functional and genomic data
Abstract
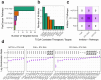
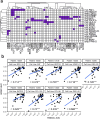
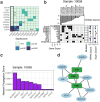
Even though head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is the seventh most common cancer worldwide, there are only two PD-1 targeted immunotherapies (pembrolizumab and nivolumab) and one tumor intrinsic EGFR targeted therapy (cetuximab) that are FDA approved for treatment of HNSCC. Taking advantage of a high throughput inhibitor assay and computational tools originally showing success in leukemia, we designed and employed HNSCC-specific inhibitor panels that capture the diversity of aberrational pathways in HNSCC to test viable cells derived from patients' HNSCC tumors. This provides a functional context to the multi-omic readouts conducted on these samples (mutations, protein expression and copy number alterations). In addition to generating these deeply characterized functional genomics datasets, we also developed additional visual analytics that have the potential to provide greater insight into HNSCC drug response patterns and potentially aid precision oncology tumor boards in evaluation and assessment of effective targeted therapeutic agents.
Keywords: Antitumor drug screening assays; HNSCC; Multi-Omics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer consensus statement on immunotherapy for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (HNSCC).J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Jul 15;7(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0662-5. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31307547 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
EGFR Alterations Influence the Cetuximab Treatment Response and c-MET Tyrosine-Kinase Inhibitor Sensitivity in Experimental Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas.Pathol Oncol Res. 2021 May 3;27:620256. doi: 10.3389/pore.2021.620256. eCollection 2021. Pathol Oncol Res. 2021. PMID: 34257586 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) as a novel mechanism of EGFR inhibitor resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patient-derived models.Cancer Biol Ther. 2018;19(10):921-933. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1451285. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29856687 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular genetics of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Curr Opin Oncol. 2019 May;31(3):131-137. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000536. Curr Opin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30893149 Review.
-
Genomics and precision surgery for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2020 Jul 1;481:45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.04.004. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 32272147 Review.
References
-
- Cancer of the Oral Cavity and Pharynx - Cancer Stat Facts.
-
- Miquel Dominguez, A. et al. Incidence, prevalence, and survival of head and neck cancers in the united Kingdom from 2000–2021. MedRxiv. 10.1101/2024.12.05.24318538 (2024).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

