Islet delta-cell architecture is remodelled in the human pancreas during type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 40473678
- PMCID: PMC12141693
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-04471-w
Islet delta-cell architecture is remodelled in the human pancreas during type 1 diabetes
Abstract
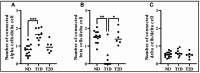
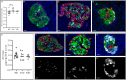
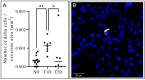
Delta cells participate in regulating hormone secretion in adjacent alpha- and beta cells and a general assumption is that cells with a shorter distance to the secreting cell receive a higher concentration of the secretory compounds. Isolated islets obtained from donors with type 1 diabetes have a reduced glucagon secretion during low glucose levels, but adding a somatostatin receptor inhibitor increases the glucagon secretion. Despite this, information regarding the delta-cell architecture during diabetes is sparse. The aim of the current study was to determine intra-islet and extra-islet delta-cell architecture in the pancreas during long-standing type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes. Pancreatic tissue from nine donors with long-standing type 1 diabetes, six donors with type 2 diabetes, and 13 donors without diabetes were obtained. Sections co-stained for somatostatin, glucagon, and insulin were manually examined. There was an approximately two-fold higher number of alpha cells directly adherent to delta cells in subjects with type 1 diabetes compared with non-diabetic subjects. The delta cells were more peripherally located within the islets of donors with type 1 diabetes. The density of extra-islet single delta cells in the acinar region was more than three-fold higher in type 1 diabetes compared with non-diabetic subjects. No differences in delta-cell architecture could be determined in type 2 diabetes compared to non-diabetic subjects. In conclusion, the islet delta-cell architecture in human type 1 diabetes is remodelled. The higher number of alpha cells directly adherent to delta cells in type 1 diabetes likely increases the alpha cells' exposure to somatostatin. This finding may be a link partly explaining the reduced glucagon response to hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes.
Keywords: Alpha cell; Delta cell; Hypoglycemia; Somatostatin; Type 1 diabetes; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

