Temperature responsive aluminum manganese doped carbon dot sensors for enhanced electrical conductivity with DFT calculations
- PMID: 40473774
- PMCID: PMC12141579
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-04531-1
Temperature responsive aluminum manganese doped carbon dot sensors for enhanced electrical conductivity with DFT calculations
Abstract
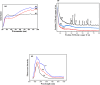
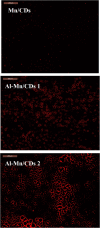
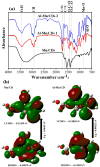
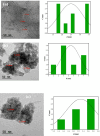
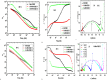
Agricultural wastes provide abundant cellulosic by-products, making them excellent candidates for sustainable material production. In this study, sugarcane bagasse was used to synthesize aluminum/manganese-doped carbon quantum dots (Al-Mn/CQDs) through a microwave-assisted process. Aluminum doping and subsequent thermal treatment progressively reduced the band gap of manganese-doped carbon quantum dots from 1.21 eV to 0.7 eV and 0.3 eV, respectively, demonstrating a tunable electronic structure with implications for applications requiring specific emission wavelengths. The resulting CQDs exhibit a spherical morphology (1.95-2.05 nm) and, upon aluminum incorporation, form uniform sheet-like structures decorated with these particles. Optical analysis shows a notable improvement in fluorescence quantum yield, reaching up to 42.65% at elevated synthesis temperatures, and a narrow full width at half maximum, demonstrating strong potential for bioimaging and sensing applications. Aluminum incorporation into Mn/CQDs lowers the LUMO energy level from - 0.12459 to - 0.14838 eV, indicating that aluminum creates or modifies acceptor states to favor electron acceptance. Moreover, the total energy decreases from - 1638.16 au in Mn/CQDs to - 1874.34 au in Al-Mn/CQDs, underscoring the enhanced stability and favorable formation of the aluminum-modified carbon dots. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations reveal a lower energy gap (0.0482 eV), higher softness (20.74 eV), and enhanced charge transfer, findings confirmed by stable and low-impedance conductivity across a wide frequency range. These properties make Al-Mn/CQDs ideal for antistatic protection, electromagnetic interference shielding, and RLC bridge calibration, while their temperature-sensitive behavior also shows promise for temperature sensing applications.
Keywords: Agricultural waste valorization; Aluminum/manganese-doped carbon quantum dots (Al-Mn/CQDs); Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC); Electrical conductivity; Microwave-assisted synthesis; Sugarcane bagasse.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Brockway, P. E., Owen, A., Brand-Correa, L. I. & Hardt, L. Estimation of global final-stage energy-return-on-investment for fossil fuels with comparison to renewable energy sources. Nat. Energy. 4, 612–621 (2019). - DOI
-
- Johnsson, F., Kjärstad, J. & Rootzén, J. The threat to climate change mitigation posed by the abundance of fossil fuels. Clim. Policy. 19, 258–274 (2019). - DOI
-
- Jin, L. et al. Integration of battery and hydrogen energy storage systems with small-scale hydropower plants in off-grid local energy communities. Energy. Conv. Manag.286, 117019 (2023). - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

