Information propagation through enzyme-free catalytic templating of DNA dimerization with weak product inhibition
- PMID: 40473818
- PMCID: PMC12313520
- DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-01831-x
Information propagation through enzyme-free catalytic templating of DNA dimerization with weak product inhibition
Abstract
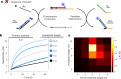
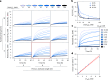
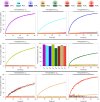
Information propagation by sequence-specific, template-catalysed molecular assembly is a key process facilitating life's biochemical complexity, yielding thousands of sequence-defined proteins from only 20 distinct building blocks. However, exploitation of catalytic templating is rare in non-biological contexts, particularly in enzyme-free environments, where even the template-catalysed formation of dimers is challenging. Typically, product inhibition-the tendency of products to bind to templates more strongly than individual monomers-prevents catalytic turnover. Here we present a rationally designed enzyme-free system in which a DNA template catalyses, with weak product inhibition, the production of sequence-specific DNA dimers. We demonstrate selective templating of nine different dimers with high specificity and catalytic turnover, then we show that the products can participate in downstream reactions, and finally that the dimerization can be coupled to covalent bond formation. Most importantly, our mechanism demonstrates a design principle for constructing synthetic molecular templating systems, a first step towards applying this powerful motif in non-biological contexts to construct many complex molecules and materials from a small number of building blocks.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
The Lived Experience of Autistic Adults in Employment: A Systematic Search and Synthesis.Autism Adulthood. 2024 Dec 2;6(4):495-509. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0114. eCollection 2024 Dec. Autism Adulthood. 2024. PMID: 40018061 Review.
-
High-throughput library transgenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans via Transgenic Arrays Resulting in Diversity of Integrated Sequences (TARDIS).Elife. 2023 Jul 4;12:RP84831. doi: 10.7554/eLife.84831. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37401921 Free PMC article.
-
Can a Liquid Biopsy Detect Circulating Tumor DNA With Low-passage Whole-genome Sequencing in Patients With a Sarcoma? A Pilot Evaluation.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jan 1;483(1):39-48. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003161. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 38905450
-
Perceptions and experiences of the prevention, detection, and management of postpartum haemorrhage: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 27;11(11):CD013795. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013795.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 38009552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crick, F. Central dogma of molecular biology. Nature227, 561–563 (1970). - PubMed
-
- Anfinsen, C. B. Principles that govern the folding of protein chains. Science181, 223–230 (1973). - PubMed
-
- Michaelis, J., Roloff, A. & Seitz, O. Amplification by nucleic acid-templated reactions. Org. Biomol. Chem.12, 2821–2833 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- URF\R\211020/Royal Society
- RG160606/Royal Society
- 851910/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
- EP/P02596X/1/RCUK | Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

