The Finite Absorption Time Concept Guiding Model Informed Drug & Generics Development in Clinical Pharmacology
- PMID: 40473892
- PMCID: PMC12222261
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-025-03878-4
The Finite Absorption Time Concept Guiding Model Informed Drug & Generics Development in Clinical Pharmacology
Abstract
Purpose: To show the implications of the incorporation of the Finite Absorption Time (F.A.T.) concept in drug development plans and in generics development and assessment and to examine regulatory implications.
Methods: Reexamining and reanalyzing published pharmacokinetic data using the pertinent models that are based on F.A.T.
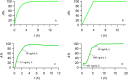
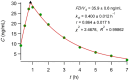
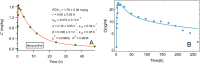
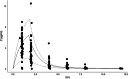
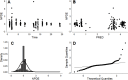
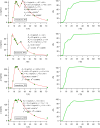
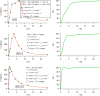
Results: Comparing absorption metrics, old and new ones, shows distinct advantages and better accuracy for those based on the F.A.T.
Conclusion: The proposed approaches can be applied successfully in all phases of drug/generics development and guide changes in their strategy and in the relevant regulatory framework.
Keywords: Bioequivalence; Finite absorption time; IVIVC; Oral drugs; Pharmacokinetics; Physiologically based finite time pharmacokinetic models.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- FDA. On January 7, 1977, FDA issued final regulations in part 320 (21 CFR 320) establishing definitions and requirements for BA and BE studies (42 FR 1624).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

