Distinct functional domains of Dystroglycan regulate inhibitory synapse formation and maintenance in cerebellar Purkinje cells
- PMID: 40473926
- PMCID: PMC12141699
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-08323-1
Distinct functional domains of Dystroglycan regulate inhibitory synapse formation and maintenance in cerebellar Purkinje cells
Abstract
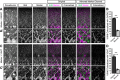
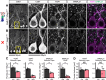
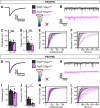
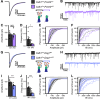
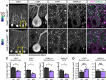
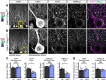
Dystroglycan is a cell adhesion molecule that localizes to synapses throughout the nervous system. While Dystroglycan is required to maintain inhibitory synapses from cerebellar molecular layer interneurons (MLIs) onto Purkinje cells (PCs) whether initial synaptogenesis during development is dependent on Dystroglycan has not been examined. We show that mice with conditional deletion of Dystroglycan from Purkinje cells prior to synaptogenesis results in impaired MLI:PC synapse formation and function due to reduced presynaptic inputs and abnormal postsynaptic GABAA receptor clustering. Using genetic manipulations that disrupt glycosylation of Dystroglycan or truncate its cytoplasmic domain, we show that Dystroglycan's role in synapse function requires both extracellular and intracellular interactions, whereas synapse formation requires only extracellular interactions. Together, these findings provide molecular insight into the mechanism of inhibitory synapse formation and maintenance in cerebellar cortex.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
Distinct functional domains of Dystroglycan regulate inhibitory synapse formation and maintenance in cerebellar Purkinje cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 30:2024.08.29.610348. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.29.610348. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Commun Biol. 2025 Jun 5;8(1):878. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-08323-1. PMID: 39257744 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Colognato, H. et al. Identification of dystroglycan as a second laminin receptor in oligodendrocytes, with a role in myelination. Development134, 1723–1736 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Tian, M. et al. Dystroglycan in the cerebellum is a laminin α2-chain binding protein at the glial-vascular interface and is expressed in Purkinje cells. Eur. J. Neurosci.8, 2739–2747 (1996). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F31 NS120649/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX004938/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- I01 BX006921/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- NA/Muscular Dystrophy Association (Muscular Dystrophy Association Inc.)
- W81XWH-18-1-0598/U.S. Department of Defense (United States Department of Defense)
- P30 NS061800/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS091027/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS126247/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS126247/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- R01NS091027/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- I01-BX004938/U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (Department of Veterans Affairs)
- F31NS120649/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- R01 NS131299/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

