18-membered macrocycle appended on resin for selective rare earth element extraction and separation
- PMID: 40473929
- PMCID: PMC12141661
- DOI: 10.1038/s42004-025-01565-4
18-membered macrocycle appended on resin for selective rare earth element extraction and separation
Abstract
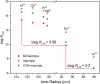
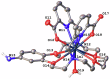
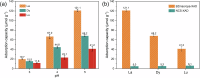
The rare earth elements are critically important for a wide range of modern technologies. However, obtaining them selectively and efficiently from natural sources and recycled materials is challenging and often requires harsh or wasteful conditions. Here we show that a macrocyclic chelator appended to a solid resin can overcome this challenge by acting as a robust platform for both the extraction and separation of these elements. This resin preferably captures the large rare earth elements in mixtures of these ions, giving rise to higher extraction efficiencies for them over the smaller ions. We further demonstrate that this resin can be used to separate rare earth elements. As a proof-of-principle validation, this resin was demonstrated to selectively extract rare earth elements in the presence of many different types of competing metal ions in a bioleachate solution obtained from autoslag waste, leading to their enrichment.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: A.M.S. and S.M. are co-founders of and hold equity in REEgen Inc., a company that recovers and manufactures REE and other critical metals. B.P. and K.I. hold options for equity in REEgen. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Rare Earth Coordination Chemistry: Fundamentals and Applications (ed. Huang, C.) (Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2008).
-
- Jha, A. R. Chapter 1: History and Discovery of Rare Earth Elements. In Rare Earth Materials Properties and Application (ed. Jha, A. R.) 14–38 (Talyor & Francis Groups, 2014).
-
- Balaram, V. Rare earth elements: a review of applications, occurrence, exploration, analysis, recycling, and environmental impact. Geosci. Front.10, 1285–1303 (2019). - DOI
-
- Cuadros-Muñoz, J. R., Jimber-del-Río, J. A., Sorhegui-Ortega, R., Zea-De la Torre, M. & Vergara-Romero, A. Contribution of rare earth elements is key to the economy of the future. Land (Basel)13, 1220 (2024).
-
- Koltun, P. & Tharumarajah, A. Life cycle impact of rare earth elements. ISRN Metall.2014, 907536 (2014). - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

