Identification and expression analysis of the cysteine synthase (CSase) gene family in Brassica napus L. under abiotic stress
- PMID: 40474087
- PMCID: PMC12139137
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-025-06532-8
Identification and expression analysis of the cysteine synthase (CSase) gene family in Brassica napus L. under abiotic stress
Abstract
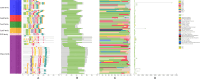
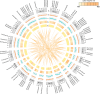
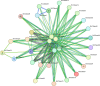
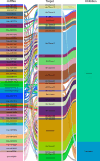
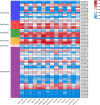
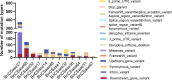
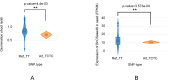
Cysteine is the first organic compound identified in plants that contains both sulfur and nitrogen. It serves as a precursor for sulfur-containing metabolites such as methionine, glutathione (GSH), and Fe-S clusters, all of which play crucial roles in plant growth, development, and stress responses. Cysteine synthase (CSase) catalyzes the final step in cysteine biosynthesis; therefore, studying the CSase gene family is essential for understanding its role in plant abiotic stress tolerance. Using the CSase protein sequences of Arabidopsis thaliana as seed sequences and integrating protein domain information, 69 members of the BnCSase gene family were identified from the whole genome of Brassica napus ZS11. These members were analyzed for their physicochemical properties, phylogenetic relationships, covariance relationships, protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks, associated miRNAs, and SNP variations. Based on transcriptome data, the expression patterns of BnCSase genes under different abiotic stress treatments were investigated. Furthermore, the relative expression levels of several BnCSase genes were analyzed under salt, alkali, low nitrogen, and drought stress treatments at 0, 6, 12, and 24 h using qRT-PCR to explore their roles in abiotic stress tolerance in B. napus. The results revealed distinct expression patterns of BnCSase genes in response to different abiotic stress signals, indicating stress-specific responses in B. napus. This study provides a theoretical basis for elucidating the functions and molecular genetic mechanisms of the BnCSase gene family in abiotic stress tolerance in rapeseed.
Keywords: Brassica napus L.; Abiotic stress; Cysteine synthase; Gene family.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Study complied with local and national regulations for using plants. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




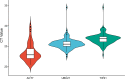
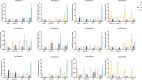
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U22A20469/the Natural Science Foundation of China
- U22A20469/the Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022ZD04010/Biological Breeding Special
- 2016YFD0100202-25/The National Key Research and Development Program
- 06270015/The Project for Building the Unique Biological and Natural Resources Database of the Hanjiang River Basin Hubei Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

