Sodium bicarbonate in treating lactic and non-lactic metabolic acidosis at different chloride levels: a retrospective study
- PMID: 40474112
- PMCID: PMC12139307
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-025-05815-1
Sodium bicarbonate in treating lactic and non-lactic metabolic acidosis at different chloride levels: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Sodium bicarbonate is commonly used to correct metabolic acidosis in pediatric patients, yet its efficacy remains controversial. This study aims to assess its effectiveness in treating non-lactic and lactic metabolic acidosis and its impact at various chloride levels.
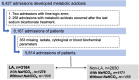
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted by screening pediatric patients diagnosed with metabolic acidosis from a paediatric intensive care database. Patients were categorized into two groups: lactate patients (lactate > 2.0 mmol/L) and non-lactate patients (lactate ≤ 2.0 mmol/L). The risk of death in patients who received sodium bicarbonate was assessed.
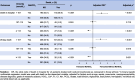
Results: Sodium bicarbonate treatment did not significantly affect in-hospital mortality in either overall lactate patients or non-lactate patients, with adjusted OR of 1.044 (95% CI: 0.829-1.315, p = 0.714) and 0.838 (95% CI: 0.548-1.281, p = 0.414), respectively. In lactate patients, those receiving sodium bicarbonate had a higher risk of in-hospital death when chloride was < 107 mmol/L (adjusted OR = 2.195, 95% CI: 1.536-3.135, p < 0.001), whereas the risk of in-hospital death decreased when chloride was ≥ 113 mmol/L (adjusted OR = 0.365, 95% CI: 0.217-0.614, p < 0.001). Similar findings were observed in non-lactate patients.
Conclusions: Sodium bicarbonate treatment does not improve the survival of pediatric patients with lactate or non-lactate metabolic acidosis. However, it can reduce the odds of mortality in pediatric patients with hyperchloremia, regardless of their lactate levels. Prospective studies are needed to further confirm these findings.
Keywords: Chloride; Lactate; Metabolic acidosis; Pediatric; Sodium bicarbonate.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Clinical efficacy of sodium bicarbonate in treating pediatric metabolic acidosis with varying level of acid-base balance parameters: a real-world study.BMC Med. 2023 Nov 29;21(1):473. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-03189-8. BMC Med. 2023. PMID: 38031038 Free PMC article.
-
Lactate Clearance and Vasopressor Seem to Be Predictors for Mortality in Severe Sepsis Patients with Lactic Acidosis Supplementing Sodium Bicarbonate: A Retrospective Analysis.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 21;10(12):e0145181. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145181. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26692209 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of sodium bicarbonate administration on mortality in patients with lactic acidosis: a retrospective analysis.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 5;8(6):e65283. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065283. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23755210 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic acidosis in childhood: why, when and how to treat.J Pediatr (Rio J). 2007 May;83(2 Suppl):S11-21. doi: 10.2223/JPED.1616. Epub 2007 May 15. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2007. PMID: 17508091 Review.
-
Sodium bicarbonate for the treatment of lactic acidosis.Chest. 2000 Jan;117(1):260-7. doi: 10.1378/chest.117.1.260. Chest. 2000. PMID: 10631227 Review.
References
-
- Jaber S, Paugam C, Futier E, Lefrant JY, Lasocki S, Lescot T, et al. Sodium bicarbonate therapy for patients with severe metabolic acidaemia in the intensive care unit (BICAR-ICU): a multicentre, open-label, randomized controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2018;392:31–40. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31080-8. - PubMed
-
- Fujii T, Udy A, Licari E, Romero L, Bellomo R. Sodium bicarbonate therapy for critically ill patients with metabolic acidosis: a scoping and a systematic review. J Crit Care. 2019;51:184–91. 10.1016/j.jcrc.2019.02.027. - PubMed
-
- Lo KB, Garvia V, Stempel JM, Ram P, Rangaswami J. Bicarbonate use and mortality outcome among critically ill patients with metabolic acidosis: a meta analysis. Heart Lung. 2020;49(2):167–74. 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2019.10.007. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

