Digital healthy eating literacy: its role in sustainable food choices and mediterranean diet adherence
- PMID: 40474141
- PMCID: PMC12142959
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-025-23353-4
Digital healthy eating literacy: its role in sustainable food choices and mediterranean diet adherence
Abstract
Background: The rise of digital platforms as sources of nutrition information has highlighted the need for digital healthy eating literacy to ensure informed dietary choices. Understanding the role of digital healthy eating literacy in shaping sustainable dietary behaviours is crucial for promoting both individual and planetary health. This study aimed to examine the associations between digital healthy eating literacy, environmentally responsible food choices, and adherence to the Mediterranean diet (MedDiet), a sustainable dietary model, among adults in Türkiye.
Methods: A total of 1,516 adults (mean age: 28.9 ± 9.8 years) residing in Türkiye were recruited through an online survey distributed via social platforms. Participants completed an online questionnaire comprising the e-Healthy Diet Literacy (e-HDL) Questionnaire, the Environmentally Responsible Food Choice Scale, and the 14-item Mediterranean Diet Adherence Screener (MEDAS). This cross-sectional study employed multivariable regression analyses to examine the associations between digital healthy eating literacy, environmentally responsible food choices, and adherence to the MedDiet.
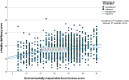
Results: Higher e-HDL scores were significantly associated with increased environmentally responsible food choices (β = 0.283, 95% CI: 0.233-0.333, p < 0.001) and a 1.039-fold increase in the odds of adherence to the MedDiet (95% CI: 1.021-1.058, p < 0.001). The strength of the association between e-HDL and the outcomes varied by subgroup, with stronger associations observed for environmentally responsible food choices among non-smokers, non-drinkers, daily exercisers, and higher-income individuals, and for adherence to the MedDiet among women, non-smokers, non-drinkers, and those with lower or equal income levels. Among the MedDiet adherents, e-HDL explained 10.5% of the variance in environmentally responsible food choices (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: This study highlights the potential importance of digital healthy eating literacy in relation to sustainable dietary behaviours and environmental health. Targeted digital nutrition education programmes may help support improvements in digital healthy eating literacy and encourage sustainable diets, supporting planetary health. Future policies should focus on increasing awareness and accessibility of reliable nutrition information on digital platforms to improve dietary practices and environmental sustainability.
Keywords: Digital nutrition literacy; Environmentally responsible food choices; Health literacy; Mediterranean diet; Planetary health; Sustainable diets.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study has been approved by the Erciyes University Social and Humanities Science Ethics Committee (Date: 31 October 2023 and Approval Number: 2023/443). All procedures were conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and informed consent was obtained from all participants electronically. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Declaration of generative AI in scientific writing: During the preparation of this work, the authors used ChatGPT in order to enhance readability and refine language. After using this tool, the authors carefully reviewed and edited the content as needed and take full responsibility for the content of the publication. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Eldesouky A, Mesias FJ, Escribano M. Perception of spanish consumers towards environmentally friendly labelling in food. Int J Consumer Stud. 2020;44(1):64–76. 10.1111/ijcs.12546.
-
- Hartmann C, Lazzarini G, Funk A, Siegrist M. Measuring consumers’ knowledge of the environmental impact of foods. Appetite. 2021;167:105622. 10.1016/j.appet.2021.105622. - PubMed
-
- Lee Y, Kim T, Jung H. Effects of university students’ perceived food literacy on ecological eating behavior towards sustainability. Sustainability. 2022;14(9):5242.
-
- Kabasakal-Cetin A, Aksaray B, Sen G. The role of food literacy and sustainable and healthy eating behaviors in ultra-processed foods consumption of undergraduate students. Food Qual Prefer. 2024;119:105232. 10.3390/su14095242.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical