PD-1-dependent therapeutic effect of Trichinella spiralis cystatin on myocardial infarction in a mice model
- PMID: 40474292
- PMCID: PMC12142987
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-025-06854-4
PD-1-dependent therapeutic effect of Trichinella spiralis cystatin on myocardial infarction in a mice model
Abstract
Background: Ischemia-induced inflammation is the primary pathological mechanism underlying cardiac tissue injury caused by myocardial infarction (MI). Trichinella spiralis cystatin (Ts-Cys) has been shown to regulate macrophage polarization and alleviate various inflammatory and immune-related diseases. Programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) is a crucial checkpoint receptor molecule and highly involved in maintaining immune tolerance. In this study, our aims were to investigate whether recombinant Ts-Cys protein (rTs-Cys) could be used to treat MI with recruited macrophage-dominant myocardial inflammation and whether PD-1 is involved in the immunomodulation of Ts-Cys in inflammatory diseases.
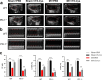
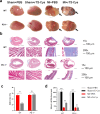
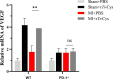
Methods: MI models were established in wild-type (WT) and PD-1 knockout (PD-1-/-) mice, followed by the intraperitoneal injection of rTs-Cys. The survival rates of mice were observed for 28 days post-surgery and treatment. Cardiac function was assessed by echocardiography. Histopathological evaluation of heart tissue affected by infarction was conducted to examine local inflammatory cell infiltration and cardiac tissue damage. Real-time quantitative PCR was used to detect messenger RNA expression levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and the macrophage surface markers inducible nitric oxide synthase and arginase-1 in the MI area. Serological levels of cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-10 (IL-10) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), were measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Bone marrow-derived macrophages from WT and PD-1-/- mice were used to assess the effects of rTs-Cys on macrophage polarization in vitro.
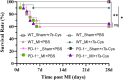
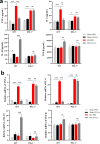
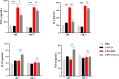
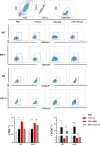
Results: In WT mice, rTs-Cys treatment significantly improved the 28-day survival rate and cardiac function, reduced local inflammatory cell infiltration and cardiac pathological damage and increased VEGF expression levels of MI mice. The therapeutic effect of rTs-Cys was associated with macrophage polarization from the pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype to the regulatory M2 phenotype with reduced levels of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6) and increased levels of regulatory cytokines (IL-10 and TGF-β), as determined by both in vivo and in vitro tests. However, this therapeutic effect of rTs-Cys on MI was significantly reduced in PD-1-/- mice, as reflected by the higher level of M1 macrophages, elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines and decreased levels of regulatory cytokines.
Conclusions: rTs-Cys promotes M2-type polarization of macrophages through the PD-1 pathway to alleviate MI in mice and is, therefore, a potential drug for the treatment of MI and other inflammation-related diseases with involvement of the PD-1 checkpoint molecule.
Keywords: Trichinella spiralis; Immunomodulation; Inflammation; Macrophage; Myocardial infarction; PD-1.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal experimental procedures are complied with the ethical guidelines of Bengbu Medical University and were approved by the Ethics Committee (Approval No. [2023]587). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Trichinella spiralis cystatin alleviates polymicrobial sepsis through activating regulatory macrophages.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Aug;109:108907. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108907. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35691271
-
Excretory/secretory products from Trichinella spiralis adult worms ameliorate myocardial infarction by inducing M2 macrophage polarization in a mouse model.Parasit Vectors. 2023 Oct 16;16(1):362. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-05930-x. Parasit Vectors. 2023. PMID: 37845695 Free PMC article.
-
Excretory/Secretory Products From Trichinella spiralis Adult Worms Attenuated DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice by Driving PD-1-Mediated M2 Macrophage Polarization.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 2;11:563784. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.563784. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33117347 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effect of Schistosoma japonicum cystatin on bacterial sepsis in mice.Parasit Vectors. 2017 May 8;10(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2162-0. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 28482922 Free PMC article.
-
Schistosoma japonicum cystatin alleviates paraquat poisoning caused acute lung injury in mice through activating regulatory macrophages.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024 Aug;281:116615. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116615. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024. PMID: 38905933
References
-
- Murphy A, Goldberg S. Mechanical complications of myocardial infarction. Am J Med. 2022;135:1401–9. - PubMed
-
- Lindahl B, Mills NL. A new clinical classification of acute myocardial infarction. Nat Med. 2023;29:2200–5. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj A, Sethi A, Rathor P, et al. Acute complications of myocardial infarction in the current era: diagnosis and management. J Investig Med. 2015;63:844–55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Byycx23089/Postgraduate Scientific Research Innovation Program of Bengbu Medical University
- 202410367009/National College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program Project
- 2024AH051189/Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Educational Committee
- 2024AH040195/Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Educational Committee
- 2023byzd028/Science Research Project of Bengbu Medical University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

