Stretchable, Multiplexed, and Bimodal Sensing Electronic Armor for Colonoscopic Continuum Robot Enhanced by Triboelectric Artificial Synapse
- PMID: 40474423
- PMCID: PMC12369696
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.202502203
Stretchable, Multiplexed, and Bimodal Sensing Electronic Armor for Colonoscopic Continuum Robot Enhanced by Triboelectric Artificial Synapse
Abstract
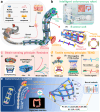
Colonoscopic continuum robots often lack sensing capabilities, risking tissue damage. An ideal robot electronic skin should offer full-body coverage, multiplexing, stretchability, and multifunctionality, but integration is challenging due to the robot's elongated structure. This work presents a stretchable electronic armor (E-armor) with a 3D crosslinked structure that enables 300 mm full coverage while accomplishing multiplexed simultaneous tactile and strain sensing through bioinspired artificial synapse mechanisms. The E-armor integrates 48 tactile sensing points through bilayer co-electrode strategy, reducing wiring while combining triboelectric encoding intelligence with innovative stretchable triboelectric interlinked films (TIFs) to form a triboelectric artificial synapse that generates digitally encoded signal pairs upon contact. A convolutional neural network and long short-term memory network (CNN-LSTM) deep learning framework achieve 99.31% accuracy in identifying multi-point tactile signals. A sodium alginate/polyacrylamide/sodium chloride (SA/PAM/NaCl) conductive hydrogel serves as a strain sensing element, providing excellent stretchability and biocompatibility, and allowing precise inference of bending angles at 12 strain sensing edges. A compliance control strategy coordinates tactile and strain signals to autonomously adjust continuum robot postures while ensuring smooth operation. The digital twin-based 3D visualization interface enhances human-robot interaction by digitally reconstructing both tactile and strain feedback, enabling real-time visualization of the continuum robot's intracolonic posture.
Keywords: colonoscopic continuum robot; full‐coverage; multiplex; strain sensing; stretchable electronic armor; tactile sensing; triboelectric encoding.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Materials published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
A Highly Stretchable, Conductive, and Transparent Bioadhesive Hydrogel as a Flexible Sensor for Enhanced Real-Time Human Health Monitoring.Adv Mater. 2024 Aug;36(35):e2404225. doi: 10.1002/adma.202404225. Epub 2024 Jul 6. Adv Mater. 2024. PMID: 38970527 Free PMC article.
-
Biomimetic Electronic Skin Based on a Stretchable Ionogel Mechanoreceptor Composed of Crumpled Conductive Rubber Electrodes for Synchronous Strain, Pressure, and Temperature Detection.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Apr 24;16(16):21341-21355. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c01899. Epub 2024 Apr 9. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38592053
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Advances and future perspectives in hydrogel-based sensing technologies: a comprehensive review.Nanotechnology. 2025 Aug 21;36(34). doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/adf8f3. Nanotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40774289 Review.
References
-
- Siegel R. L., Wagle N. S., Cercek A., Smith R. A., Jemal A., CA ‐ Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 233. - PubMed
-
- Gan P., Li P., Xia H., Zhou X., Tang X., Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 46, 203. - PubMed
-
- Rex D. K., Schoenfeld P. S., Cohen J., Pike I. M., Adler D. G., Fennerty M. B., Lieb J. G., Park W. G., Rizk M. K., Sawhney M. S., Shaheen N. J., Wani S., Weinberg D. S., Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 72. - PubMed
-
- Hadi Hosseinabadi A. H., Salcudean S. E., Int. J. Robot. Res. 2022, 41, 136.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

