Systematic reviewers' perspectives on sharing review data, analytic code, and other materials: A survey
- PMID: 40474910
- PMCID: PMC11795976
- DOI: 10.1002/cesm.12008
Systematic reviewers' perspectives on sharing review data, analytic code, and other materials: A survey
Abstract
Background: There are many benefits of sharing data, analytic code, and other materials, yet these items are infrequently shared among systematic reviews (SRs). It is unclear which factors influence authors' decisions to share data, code, or materials when publishing their SRs. Therefore, we aimed to explore systematic reviewers' perspectives on the importance of sharing review materials and factors that might influence such practices.
Methods: We searched PubMed for SRs published from January to April 2021, from which we randomly allocated 50% to this survey and 50% to another survey on the replication of SRs. We sent an electronic survey to authors of these SRs (n = 4671) using Qualtrics. Quantitative responses were summarized using frequency analysis. Free-text answers were coded using an inductive approach.
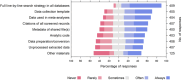
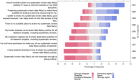
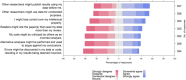
Results: The response rate was 9% (n = 417). Most participants supported routine sharing of search strategies (84%) but fewer for analytic code (43%) or files documenting data preparation (38%). Most participants agreed that normative practices within the discipline were an important facilitator (78%). Major perceived barriers were lack of time (62%) and suitable sharing platforms (31%). Few participants were required by funders (19%) or institutions (17%) to share data, and only 12% of participants reported receiving training on data sharing. Commonly perceived consequences of data sharing were lost opportunities for future publications (50%), misuse of data (48%), and issues with intellectual property (40%). In their most recent reviews, participants who did not share data cited the lack of journal requirements (56%) or noted the review did not include any statistical analysis that required sharing (29%).
Conclusion: Certain types of review materials were considered unnecessary for sharing, despite their importance to the review's transparency and reproducibility. Structural barriers and concerns about negative consequences hinder data sharing among systematic reviewers. Normalization and institutional incentives are essential to promote data-sharing practices in evidence-synthesis research.
© 2023 The Authors. Cochrane Evidence Synthesis and Methods published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Cochrane Collaboration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic reviewers' perspectives on replication of systematic reviews: A survey.Cochrane Evid Synth Methods. 2023 Apr 10;1(2):e12009. doi: 10.1002/cesm.12009. eCollection 2023 Apr. Cochrane Evid Synth Methods. 2023. PMID: 40474913 Free PMC article.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Data and code availability statements in systematic reviews of interventions were often missing or inaccurate: a content analysis.J Clin Epidemiol. 2022 Jul;147:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2022.03.003. Epub 2022 Mar 10. J Clin Epidemiol. 2022. PMID: 35278609
-
Reproducible research practices are underused in systematic reviews of biomedical interventions.J Clin Epidemiol. 2018 Feb;94:8-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.10.017. Epub 2017 Nov 4. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018. PMID: 29113936 Review.
References
-
- Alston JM, Rick JA. A beginner's guide to conducting reproducible research. Bull Ecol Soc Am. 2021;102:e01801. 10.1002/bes2.1801 - DOI
-
- National Institutes of Health . NOT‐OD‐21‐013: Final NIH Policy for Data Management and Sharing. https://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/notice-files/NOT-OD-21-013.html
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
