First Clinical Implementation of Step-and-Shoot Proton Arc Therapy for Head and Neck Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 40474940
- PMCID: PMC12138570
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpt.2025.100749
First Clinical Implementation of Step-and-Shoot Proton Arc Therapy for Head and Neck Cancer Treatment
Abstract
Purpose: Dynamic Spot-scanning Proton Arc (SPArc-Dynamic) therapy has gained attention for enhancing dosimetric plan quality. However, its full clinical implementation remains under development. As an interim milestone, we developed step-and-shoot arc therapy (SPArc-step&shoot) for head-neck cancer treatment.
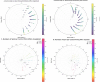
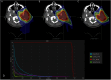
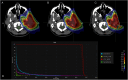
Patients and methods: An in-house spot and energy-layer sparsity optimization algorithm was integrated into a clinical treatment planning system. The algorithm prioritized higher MU-weighted energy layers and spots to ensure delivery efficiency and superior plan quality while meeting machine requirements (≥0.02MU/spot). A Dynamic SPArc simulator calculated delivery times, and a machine-learning-based synthetic CT(synCT) platform monitored dose robustness. In June 2024, a head-neck cancer patient with parotid gland malignancy was treated using SPArc-step&shoot (6600 cGy[relative biological effectiveness] in 33 fx) with 9 static fields at 20-degree intervals. Comparative plans (SFO-IMPT, SPArc-Dynamic) were evaluated for dose metrics, delivery times, and adaptive planning.
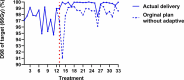
Results: SPArc-step&shoot and SPArc-Dynamic showed similar target coverage and organ-at-risks sparing, and the plan quality is superior to the 3-field SFO-IMPT in the brainstem, oral cavity, and spinal cord sparing. The simulated continuous arc delivery time is 15.9, 6.32, and 4.31 minutes for SPArc-step&shoot, SFO-IMPT, and SPArc-Dynamic, respectively. The actual recorded average treatment delivery time for SPArc-step&shoot in 33 fx is 16.7 ± 1.56 minutes. QA-CT and synCT showed a similar target coverage degradation and perturbation, and a replan was initiated.
Conclusion: The SPArc-step&shoot therapy was successfully implemented in the clinical settings, and first patient was successfully treated between June and August 2024. The synCT platform serves a critical role in the daily monitoring process as SPArc-Dynamic might be more sensitive to the patient geometry changes in HNC treatment.
Keywords: Adaptive planning; Neck-neck cancer; Step-and-shoot proton arc therapy.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Particle Therapy Co-operative Group.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Xuanfeng Ding reports financial support was provided by IBA. Xuanfeng Ding reports a relationship with Ion Beam Applications SA that includes funding grants, speaking and lecture fees, and travel reimbursement. Xuanfeng Ding has patent Particle Arc Therapy licensed to IBA. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improve the dosimetric outcome in bilateral head and neck cancer (HNC) treatment using spot-scanning proton arc (SPArc) therapy: a feasibility study.Radiat Oncol. 2020 Jan 30;15(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s13014-020-1476-9. Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32000817 Free PMC article.
-
Spot-Scanning Proton Arc (SPArc) Therapy: The First Robust and Delivery-Efficient Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016 Dec 1;96(5):1107-1116. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.08.049. Epub 2016 Sep 7. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016. PMID: 27869083
-
Spot scanning proton arc therapy reduces toxicity in oropharyngeal cancer patients.Med Phys. 2023 Mar;50(3):1305-1317. doi: 10.1002/mp.16098. Epub 2023 Jan 17. Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36373893
-
First direct machine-specific parameters incorporated in Spot-scanning Proton Arc (SPArc) optimization algorithm.Med Phys. 2024 Aug;51(8):5682-5692. doi: 10.1002/mp.16985. Epub 2024 Feb 10. Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38340368
-
A novel energy layer optimization framework for spot-scanning proton arc therapy.Med Phys. 2020 Jun;47(5):2072-2084. doi: 10.1002/mp.14083. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 32040214 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
