Antibacterial MXenes: An emerging non-antibiotic paradigm for surface engineering of orthopedic and dental implants
- PMID: 40475083
- PMCID: PMC12137176
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.05.002
Antibacterial MXenes: An emerging non-antibiotic paradigm for surface engineering of orthopedic and dental implants
Abstract
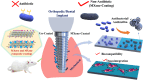
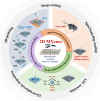
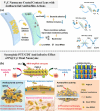
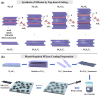
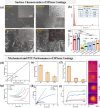
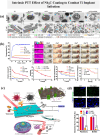
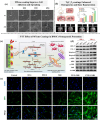
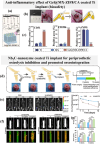
The colonization of planktonic bacteria onto implant surfaces is a serious concern in the medical field due to increasing infection-related mortality and fiscal difficulties worldwide. Various static, dynamic, and active coating techniques were established to tackle implant-associated infections (IAIs). However, the existing implant coating methods often confront issues with poor universality for different substrates, adaptability, stability, and the emergence of multi-drug resistance (MDR). The miraculous two-dimensional (2D) MXenes with outstanding multimodal bactericidal effects have been spotted as promising non-antibiotic implant surface coating additives for superior antibiofilm and osseointegration properties. This review systematically assesses the recent progress of antibacterial MXenes and their revolutionary usage to prevent peri-implantitis. We specifically sought to disclose the various forms of MXenes, such as composites, heterojunctions (HJs), and functional biomaterials used in combatting MDR and non-MDR bacterial pathogens by adopting therapeutic ventures such as photothermal therapy (PTT), photodynamic therapy (PDT), chemodynamic therapy (CDT), and sonodynamic therapy (SDT). In addition, we outlined the extension of MXene antibacterial systems for orthopedic and dental implant surface engineering to improve their longevity and safety. A thorough understanding of antibacterial MXenes synthesis, surface modification strategies, and biocompatible functional properties was deliberated to facilitate the construction of innovative coatings. Lastly, some viewpoints on the current limitations and key considerations for the future concept design of MXenes-coated implants were contemplated constructively to promote clinical outcomes.
Keywords: Antibacterial; Coatings; MXenes; Osseointegration; Peri-implantitis; Surface modification.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Gulati K., Chopra D., Kocak-Oztug N.A., Verron E. Fit and forget: the future of dental implant therapy via nanotechnology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023 - PubMed
-
- Duncan W.J., Coates D.E. Meeting the challenges and clinical requirements for dental regeneration; the New Zealand experience. Bone. 2022;154 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

