EPIDEMIOLOGICAL PROFILE OF PATIENTS WITH SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS TREATED AT A QUATERNARY HOSPITAL IN THE STATE OF SÃO PAULO
- PMID: 40475360
- PMCID: PMC12136614
- DOI: 10.1590/1413-785220253302e287081
EPIDEMIOLOGICAL PROFILE OF PATIENTS WITH SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS TREATED AT A QUATERNARY HOSPITAL IN THE STATE OF SÃO PAULO
Abstract
Objective: To report the profile of patients diagnosed with systemic sclerosis and monitored in a four-year hospital in São Paulo.
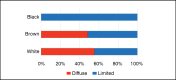
Methods: Observational study with 51 patients, mostly composed of women. Descriptive statistics such as mean age, proportions (sex, ethnicity, form of the disease), and correlations between functional scores (HAQ, SHAQ, and Rodnan score) were extracted.
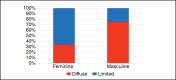
Results: The average age found was 49.96 ± 12.01 years. The time since diagnosis was 11.19 ± 10.16 years. When separated by sex, 25% of men presented the limited form, while 65.9% of women presented the localized form. There was a statistically significant correlation (p-value<0.01) between the Rodnan score and the HAQ score, with a value of 0.36 (CI: 0.09-0.58), as well as with the SHAQ score (value of 0.33; CI: 0.05-0.55, p-value=0.01). When evaluating the correlation between the Rodnan score and the Cochin functional scale, there was a statistically significant correlation (p-value<0.01), with a value of 0.38 (0.12-0.58).
Conclusion: According to the literature, this study showed the highest prevalence in women, and the predominant form is limited. Level of Evidence II; Cohort Study.
Objetivo: Relatar o perfil dos pacientes diagnosticados com esclerose sistêmica e acompanhados em um hospital quartenário paulista.
Métodos: Estudo observacional com 51 pacientes, composto majoritariamente por mulheres. Foram extraídas estatísticas descritivas como idade média, proporções (sexo, etnia, forma da doença) e correlações entre escores funcionais (HAQ, SHAQ e escore de Rodnan).
Resultados: A idade média encontrada foi de 49,96 ± 12,01 anos. O tempo desde o diagnóstico foi de 11,19 ± 10,16 anos. Quando separados por sexo, 25% dos homens apresentaram a forma limitada, enquanto 65,9% das mulheres apresentaram a forma localizada. Houve correlação estatisticamente significante (p-valor<0,01) entre o escore de Rodnan e a pontuação HAQ, com valor de 0,36 (IC: 0,09-0,58), bem como com a pontuação SHAQ (valor de 0,33; IC: 0,05-0,55, p-valor=0.01). Quando avaliada a correlação entre o escore de Rodnan e a escala funcional de Cochin, houve correlação estatisticamente significante (p-valor<0,01), com valor de 0,38 (0,12-0,58).
Conclusão: De acordo com a literatura, este estudo evidenciou a maior prevalência em mulheres e a forma predominante sendo a limitada. Nível de Evidência II; Estudo de Coorte.
Keywords: Epidemiological Profile; Epidemiology; Scleroderma, Systemic.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no potential conflict of interest related to this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessing disability and quality of life in systemic sclerosis: construct validities of the Cochin Hand Function Scale, Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ), Systemic Sclerosis HAQ, and Medical Outcomes Study 36-Item Short Form Health Survey.Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Feb 15;57(1):94-102. doi: 10.1002/art.22468. Arthritis Rheum. 2007. PMID: 17266096
-
Responsiveness of the University of California Los Angeles Scleroderma Clinical Trial Consortium gastrointestinal tract 2.0 (UCLA-SCTC-GIT 2.0)to change in scleroderma patients.J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2021 Oct;6(3):236-241. doi: 10.1177/2397198321992197. Epub 2021 Feb 22. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2021. PMID: 35387210 Free PMC article.
-
Association of pain and clinical factors on disability and quality of life in systemic sclerosis: A cross-sectional study from Turkish League Against Rheumatism Network.Arch Rheumatol. 2022 Nov 11;38(1):9-21. doi: 10.46497/ArchRheumatol.2023.9243. eCollection 2023 Mar. Arch Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 37235112 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of skin disease in scleroderma: Practices and opinions of investigators studying scleroderma.J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2020 Oct;5(3):167-171. doi: 10.1177/2397198320921044. Epub 2020 May 29. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2020. PMID: 35382518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
History of skin thickness assessment and the Rodnan skin thickness scoring method in systemic sclerosis.J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2019 Jun;4(2):83-88. doi: 10.1177/2397198318823122. Epub 2019 Jan 31. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2019. PMID: 35382394 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Delisle VC, Hudson M, Baron M, Thombs BD. The Canadian Scleroderma Research Group A. Sex and time to diagnosis in systemic sclerosis: an updated analysis of 1,129 patients from the Canadian scleroderma research group registry. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014;32((6 Suppl 86)):S-10–S-14. - PubMed
-
- Morgan ND, Shah AA, Mayes MD, Domsic RT, Medsger TA, Jr, Steen VD, et al. Clinical and serological features of systemic sclerosis in a multicenter African American cohort: Analysis of the genome research in African American scleroderma patients clinical database. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96(51):e8980. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008980. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ferraz MB. Tradução para o português e validação do questionário para avaliar a capacidade funcional "Stanford Health Assessment Questionaire". São Paulo: Paulista School of Medicine, Federal University of São Paulo (UNIFESP); 1990. [doctorate]
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources