Clinical Delivery of Whole Systems Traditional Chinese Medicine and Impacts Upon Patient Reported Outcomes During IVF
- PMID: 40475372
- PMCID: PMC12138210
- DOI: 10.1177/27536130251349116
Clinical Delivery of Whole Systems Traditional Chinese Medicine and Impacts Upon Patient Reported Outcomes During IVF
Abstract
Background: Several clinical trials support the efficacy of Whole Systems Traditional Chinese Medicine (WS-TCM) modalities, including acupuncture, for improving outcomes among women undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF), but few studies have described its real-world integration within an academic medical setting or its immediate effects on pain, stress, and anxiety.
Objective: To characterize the clinical delivery of WS-TCM and assess its effects on patient-reported outcomes (PROs) among patients receiving WS-TCM while undergoing IVF.
Methods: A retrospective review of patients who received ≥1 WS-TCM treatment associated with ≥1 embryo transfer at a single center was conducted. A linear mixed model adjusting for the random effect of patients seen over multiple treatments was used to calculate PRO changes among those with pre-treatment PROs ≥1 on a 0-10 numeric rating scale.
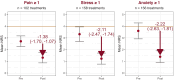
Results: 1896 WS-TCM treatments were provided during 202 embryo transfers among 146 patients. Patients (mean age 35.76 ± 4.37) were predominantly white (79.5%), and 26.7% had a documented mental health diagnosis. Of the 202 embryo transfers, 64.9% included pre-transfer treatment, 88.6% included day-of-transfer treatment, and 32.2% included post-transfer treatment. Patients reporting pre-treatment PROs ≥1 reported clinically significant mean [95% CI] reductions in pain (-1.38 [-1.70, -1.07]), stress (-2.11 [-2.47, -1.74]), and anxiety (-2.22 [-2.63, -1.81]) within a single treatment.
Conclusions: This study supports the integration of WS-TCM within IVF and its benefits for reducing acute pain, stress, and anxiety. WS-TCM may improve patient experiences and be a useful treatment for psychosocial concerns that often accompany IVF.
Keywords: acupuncture; pregnancy; traditional Chinese medicine.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- CDC . National ART summary. 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/art/reports/2020/summary.html
-
- Jain MSM. Assisted reproductive technology (ART) techniques. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023. - PubMed
-
- CDC . ART success rates. https://www.cdc.gov/art/artdata/index.html
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
