Avidity of pertussis toxin antibodies following vaccination with genetically versus chemically detoxified pertussis toxin-containing vaccines during pregnancy
- PMID: 40475765
- PMCID: PMC12137321
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1569151
Avidity of pertussis toxin antibodies following vaccination with genetically versus chemically detoxified pertussis toxin-containing vaccines during pregnancy
Abstract
Background: Both the quantity and quality of circulating anti-pertussis toxin antibodies are important for protection against severe pertussis. We compared the avidity of PT-IgG antibodies in pregnant women and their infants following vaccination during pregnancy with pertussis vaccines containing genetically-detoxified pertussis toxin (PTgen) or chemically-detoxified PT (PTchem).
Methods: We analyzed serum samples collected earlier from pregnant women (at delivery) and their infants (at birth and 2 months of age) participating in a clinical trial where pregnant women had been vaccinated during pregnancy with recombinant acellular pertussis vaccine containing 1 µg PTgen (standalone, ap1gen, [n=37], or combined to tetanus and diphtheria, Tdap1gen [n=34]), 2 µg PTgen (Tdap2gen, n=35), or 5 µg PTgen (TdaP5gen, n=34), or acellular pertussis vaccine containing 8 µg PTchem (Tdap8chem, n=35). Avidity was assessed by adding increasing concentrations (0.25, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, and 3 M) of NH4SCN as a bond-breaking agent and measuring PT-IgG levels by ELISA.
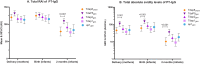
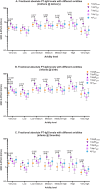
Findings: Compared with Tdap8chem, TdaP5gen vaccination was associated with significantly higher total absolute avidity (p<0.001) and medium-high to very-high avidity PT-IgG levels (p≤0.02) in mothers at delivery, infants at birth and infants at 2 months of age. Avidity was comparable to Tdap8chem after vaccination with the low-dose PTgen formulations (ap1gen, Tdap1gen or Tdap2gen). There were no differences for vaccination during the 2nd or 3rd trimester of pregnancy.
Interpretation: Compared with chemically detoxified vaccines, vaccination during pregnancy with recombinant genetically detoxified acellular pertussis vaccine at lower PT concentration provides infants with at least similar or higher quality PT-IgG antibodies. Consequently, recombinant pertussis vaccines may offer comparable or better protection against pertussis.
Keywords: avidity; genetically inactivated; maternal immunization; pertussis; pertussis toxin; recombinant vaccine; vaccination during pregnancy.
Copyright © 2025 Abu-Raya, Del Giudice, van den Biggelaar, Tang, Bhat, Pham and Wijagkanalan.
Conflict of interest statement
Author BA-R received honoraria for participation in live meetings from Sanofi Pasteur France and Canada related to pertussis and RSV. BA-R received nominal payment as a reviewer for ELSEVIER and as a member of a data and safety monitoring board for a study conducted by Chulalongkorn University (Bangkok, Thailand). BA-R is co-investigator on studies funded by GSK, Pfizer, Merck, Moderna, Vaccitech and Inventprise. All funds have been paid to his institute, and he has not received any personal payments. Authors GG and AB received consultancy honoraria from BioNet-Asia including for the published work. Authors WW and HTP are employees of BioNet-Asia. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A phase 2 randomized controlled dose-ranging trial of recombinant pertussis booster vaccines containing genetically inactivated pertussis toxin in pregnant women.Vaccine. 2023 Jul 12;41(31):4541-4553. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2023.06.001. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Vaccine. 2023. PMID: 37330371 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effective and safe transfer of maternal antibodies persisting two months postpartum following maternal immunization with different doses of recombinant pertussis-containing vaccines.Vaccine. 2024 Jan 12;42(2):383-395. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2023.11.042. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Vaccine. 2024. PMID: 38061956 Free PMC article.
-
A phase 2 randomized controlled dose-ranging trial of recombinant pertussis booster vaccines containing genetically inactivated pertussis toxin in women of childbearing age.Vaccine. 2022 Apr 1;40(15):2352-2361. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.10.076. Epub 2021 Nov 14. Vaccine. 2022. PMID: 34789403 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of Anti-PT Antibody Response after Pertussis Vaccination and Infection: The Importance of Both Quantity and Quality.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jul 21;13(8):508. doi: 10.3390/toxins13080508. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34437379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetically detoxified pertussis toxin (PT-9K/129G): implications for immunization and vaccines.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2014 Oct;13(10):1191-204. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2014.942641. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2014. PMID: 25183193 Review.
Cited by
-
Pertussis resurgence: epidemiological trends, pathogenic mechanisms, and preventive strategies.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 10;16:1618883. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1618883. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40709171 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control E . Increase of pertussis cases in the EU/EEA. Stockholm: ECDC; (2024).
-
- UK Health Security Agency . Confirmed cases of pertussis in England by month . Available online at: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/pertussis-epidemiology-in-eng... (Accessed December 1, 2024).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

