Factors influencing pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in resectable breast cancer: A retrospective study
- PMID: 40476040
- PMCID: PMC12138496
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2025.15112
Factors influencing pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in resectable breast cancer: A retrospective study
Abstract
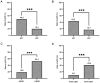
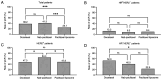
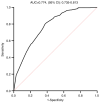
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) is widely used to treat breast cancer and a pathological complete response (pCR) following NAC is associated with an optimal prognosis; however, pCR rates vary significantly. In the present study, the effects of clinicopathological factors and the administration of different taxanes on pCR rates in patients with resectable breast cancer were assessed. A total of 552 patients with breast cancer who received NAC between May 2019 and June 2024 were included in the present study. The clinicopathological traits of the patients were retrieved from medical records and their association with the pCR rate was evaluated using univariate and multivariate regression analyses. The efficacy of nanoparticle albumin-bound (Nab)-paclitaxel, docetaxel and paclitaxel liposomes in different subtypes of breast cancer were further evaluated. A total of 189 of 552 (34.2%) patients achieved pCR following NAC. The pCR rate varied significantly among different molecular subtypes as follows: 58.9% (96/163), 40.7% (37/91), 35.6% (37/104) and 9.8% (19/298) among patients with hormone receptor (HR) negative (-) human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) positive (+), HR+HER2+, HR-HER2- and HR+HER2- breast cancer, respectively. The factors estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor and HER2 status, Ki-67 index and taxane regimen were all significantly associated with pCR in the univariate analysis. In the multivariate regression analysis, ER-, HER2+, Ki-67 index ≥30% and Nab-paclitaxel were independent predictors of pCR. The multivariate regression analysis model had an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve area under the curve of 0.774 (95% confidence interval, 0.735-0.813). The pCR rates were 41.3, 38.2 and 25.1% among the Nab-paclitaxel, docetaxel and paclitaxel liposome groups, respectively. Patients with ER-, HER2+, Ki-67 index ≥30% were associated with high pCR rates. Moreover, patients who received Nab-paclitaxel and docetaxel were more likely to achieve pCR compared with paclitaxel liposomes, particularly for those with HER2+ and HR-HER2- statuses. In conclusion, molecular subtypes (ER/HER2 status, high Ki-67) and different taxanes significantly influence pCR likelihood. Nab-paclitaxel and docetaxel were identified as effective taxanes, highlighting their potential clinical preference, especially in HER2+ and HR-HER2- breast cancer.
Keywords: breast cancer; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; pathological complete response; taxane.
Copyright: © 2025 Kang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Li Y, Song W, Gao P, Guan X, Wang B, Zhang L, Yao Y, Guo Y, Wang Y, Jiang S, Sun S. Global, regional, and national burden of breast, cervical, uterine, and ovarian cancer and their risk factors among women from 1990 to 2021, and projections to 2050: Findings from the global burden of disease study 2021. BMC Cancer. 2025;25:330. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13741-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dubsky P, Pinker K, Cardoso F, Montagna G, Ritter M, Denkert C, Rubio IT, de Azambuja E, Curigliano G, Gentilini O, et al. Breast conservation and axillary management after primary systemic therapy in patients with early-stage breast cancer: the Lucerne toolbox. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:e18–e28. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30580-5. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
