Use of cell phone data to correct Île-de-France population estimates and SARS-CoV-2 incidence, July to September, 2021: a proof-of-concept exercise
- PMID: 40476291
- PMCID: PMC12143120
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.22.2400530
Use of cell phone data to correct Île-de-France population estimates and SARS-CoV-2 incidence, July to September, 2021: a proof-of-concept exercise
Abstract
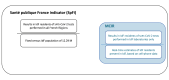
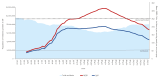
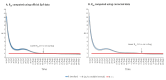
BackgroundDuring the COVID-19 pandemic, Santé publique France (SpF) published incidence (SpFi) rates based on census denominators. Denominators using cell phone connection (CPC) data can better reflect the population present and seasonal mobilities.AimGiven uncertainties regarding the actual number of Île-de-France (IdF) residents present in IdF during summer 2021, we aimed to better approximate true incidence rates from positive SARS-CoV-2 tests in IdF using CPC-derived population denominators.MethodThis longitudinal study used the daily number of positive tests (PCR and Ag) on IdF residents in IdF as the numerator and the estimated resident population present in IdF at midnight as the denominator. We computed the mean corrected incidence rate (MCIR) per moving week between 4 July and 9 September 2021.ResultsThe MCIR showed higher incidence rates than initially estimated, especially during August when residents had left IdF for the holidays. Incidence rates reached a peak on 16 August when the SpFi rate per moving week was 200.9 per 100,000 compared with 315.6 per 100,000 with the MCIR, representing a 57% increase.ConclusionUsing local SARS-CoV-2 testing data and real-time population denominators, we showed that indicators using non-geographically referenced test results and fixed population denominators that ignore seasonal mobility can significantly underestimate incidence rates in IdF. New data sources using CPC data provide the opportunity to calculate more accurate and dynamic incidence rates and to map epidemics more precisely and in real time.
Keywords: Covid-19; SARS-CoV-2; cell phone; epidemic; epidemiology; incidence; mobile phone; population; rates.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Bhopal RS. The epidemiological concept of population. In: Bhopal RS, editor. Concepts of Epidemiology: Integrating the ideas, theories, principles, and methods of epidemiology. Oxford University Press; 2016. Available from: 10.1093/med/9780198739685.003.0002 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
