Investigation of the Potential of Commercial and Wild Passiflora Seed Species as Stilbenes Sources
- PMID: 40476489
- PMCID: PMC12186530
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5c00440
Investigation of the Potential of Commercial and Wild Passiflora Seed Species as Stilbenes Sources
Abstract
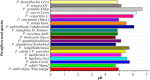
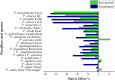
Passion fruit seeds, a byproduct of juice processing, are rich in bioactive stilbenes with health-promoting properties. This study investigated piceatannol and resveratrol in seeds from four commercial and sixteen wild Passiflora species using the μ-QuEChERS method combined with UHPLC-MS/MS analysis. The method showed good analytical performance, with linearity (R2 ≥ 0.991), LOQ ≤ 20 μg kg-1, and RSD < 11%. Piceatannol and resveratrol were found in 70 and 60% of the analyzed species, respectively. Piceatannol was found in significantly higher amounts (0.6-55.2 mg kg-1) in 95% of these species, with values up to 56 times greater than resveratrol (0.3-7.5 mg kg-1). The highest piceatannol amounts were observed in the wild species P. longifilamentosa (55.2 mg kg-1) and P. edulis x P. caerulea (44.7 mg kg-1). These findings highlight Passiflora seeds as a valuable natural source of piceatannol, supporting their potential applications in functional foods, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical products.
Keywords: Passiflora; UHPLC-MS/MS; piceatannol; resveratrol; seeds; μ-QuEChERS.
Figures


References
-
- Lucas-González R., Capanoglu E., Pateiro M., Khaneghah A. M., Hano C., Lorenzo J. M.. Current trends in Passiflora genus research: Obesity and fermented foods systematic review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022;127:143–155. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2022.07.008. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

