Matrix metalloproteinase‑9 in hemorrhagic transformation after acute ischemic stroke (Review)
- PMID: 40476578
- PMCID: PMC12175134
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13590
Matrix metalloproteinase‑9 in hemorrhagic transformation after acute ischemic stroke (Review)
Abstract
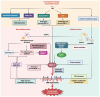
Hemorrhagic transformation (HT) is a devasting complication following acute ischemic stroke with high morbidity and mortality. The pathogenesis of HT mainly involves ischemia‑reperfusion‑induced oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, thrombolytic therapy‑associated toxicity and, most critically, blood‑brain barrier (BBB) disruption. Matrix metalloproteinase‑9 (MMP‑9) serves as a critical mediator of HT through degrading extracellular matrix components and disrupting tight junction proteins, thereby compromising BBB integrity. Thus, elaborating the underlying molecular mechanisms of MMP‑9 in destroying BBB and promoting HT is essential to improve the outcome of ischemic stroke patients. Furthermore, to provide beneficial insights for the treatment of ischemic stroke, precise understanding of the potential role of MMP‑9 as a biomarker and treatment target to predict and ameliorate the risk of HT is also necessary.
Keywords: biomarker; hemorrhagic transformation; ischemic stroke; matrix metalloproteinase‑9; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Feigin VL, Owolabi MO, World Stroke Organization-Lancet Neurology Commission Stroke Collaboration Group Pragmatic solutions to reduce the global burden of stroke: A orld stroke organization-lancet neurology commission. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22:1160–1206. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(23)00277-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Otsu Y, Namekawa M, Toriyabe M, Ninomiya I, Hatakeyama M, Uemura M, Onodera O, Shimohata T, Kanazawa M. Strategies to prevent hemorrhagic transformation after reperfusion therapies for acute ischemic stroke: A literature review. J Neurol Sci. 2020;419:117217. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2020.117217. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

