Mixed-Metal Ce-Zr-Mn Clusters as Photo-Catalysts for Decarboxylative Functionalization of Carboxylic Acids
- PMID: 40476749
- PMCID: PMC12338407
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202505639
Mixed-Metal Ce-Zr-Mn Clusters as Photo-Catalysts for Decarboxylative Functionalization of Carboxylic Acids
Abstract
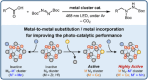
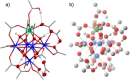
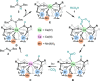
Decarboxylative hydrazination of carboxylic acids was achieved using a 1:5:2 ratio of three metal salts, Ce(OtBu)4, Zr(OtBu)4, and Mn(OAc)3, as a catalyst under visible light irradiation. The catalytic activity, compared with our previously developed Ce6 cluster photo-catalysts, was enhanced by the formation of single cerium-incorporated hexanuclear mixed-metal clusters containing a [CeZr5O4(OH)4]12+ core. The manganese salts further accelerated the overall reaction rate (10 times faster reaction rate with the manganese salt than that of the manganese-free conditions). Using the isolated cluster, CeZr5O4(OH)4(OCOCH2 tBu)12(HOCOCH2 tBu)4 (4a), with Mn(OAc)3, phenol and thiophenol-containing carboxylic acids were transformed to their decarboxylative hydrazinated products in moderate to high yields, while a mixture of Ce6O4(OH)4(OCOCH2 tBu)12(HOCOCH2 tBu)4 (4c) and Mn(OAc)3 or Ce(OtBu)4, Zr(OtBu)4, and Mn(OAc)3 yielded lower amounts of the products. These findings highlight the importance of incorporating cerium(IV) into the zirconium-based core to tolerate these easily oxidizable functional groups. Upon exposure of 4a to blue LED light under an argon atmosphere, the CeZr5 cluster produced 2,2,5,5-tetramethylhexane, a radical coupling product derived from the carboxylate ligand on 4a, in half an equivalent per cluster, consistent with the photo-reduction of cerium(IV) and inertness of the oxo- and hydroxo-bridged Zr5 motif as a metallo-ligand around the cerium(IV) site. Moreover, decarboxylative oxygenation of carboxylic acids under air followed by treatment with NaBH4 resulted in the production of one-carbon shortened alcohols in excellent yields when using Ce(OtBu)4 and Zr(OtBu)4 or Hf(OtBu)4 in a 1:5 ratio: the reaction rates were 8-10 times higher than that of the previously developed cerium-catalyzed reaction under identical conditions.
Keywords: Carboxylic acid; Cerium; Manganese; Zirconium.
© 2025 The Author(s). Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Romero N. A., Nicewicz D. A., Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10075–10166. - PubMed
-
- Twilton J., Le C., Zhang P., Shaw M. H., Evans R. W., MacMillan D. W. C., Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 1–19.
Grants and funding
- JP20H02742/JSPS KAKENHI, Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research(B)
- JP24K01486/JSPS KAKENHI, Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research(B)
- JP21K01486/JSPS KAKENHI, Grant-in-Aid for Challenging Research (Exploratory)
- JP24H01853/Green Catalysis Science for Renovating Transformation of Carbon-Based Resources
- JP23H04906/Green Catalysis Science for Renovating Transformation of Carbon-Based Resources
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

