Epidemic modeling for the resurgence of COVID-19 in Chinese local communities
- PMID: 40477617
- PMCID: PMC9085441
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jnlssr.2022.03.005
Epidemic modeling for the resurgence of COVID-19 in Chinese local communities
Abstract
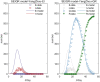
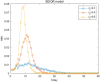
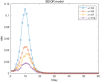
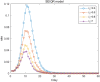
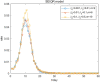
COVID-19 is a constantly challenging global health issue due to its strong intensity, rapid mutation and high infectiousness. The new Delta and Omicron variants have triggered massive outbreaks worldwide. Even China, which has done a good job in outbreak prevention, is still heavily affected by the virus. The long-term fight against multiple COVID-19 outbreaks is ongoing. In this study, we propose an SEIQR model that considers the incubation period and quarantine measurement. We verified our model using actual outbreak data from four Chinese cities. Numerical simulations show that a five-day delay results in a double resurgence scale. Our model can be used as a tool to understand the spread of the virus quantitatively and provide a reference for policymaking accordingly.
Keywords: COVID-19; Mutation; Quarantine; Resurgence; SEIQR model.
© 2022 China Science Publishing & Media Ltd. Publishing Services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co. Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this study.
Figures





References
-
- World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/data.
-
- Zhang L., Zhu J., Wang X., Yang J., Xu X.K. Characterizing COVID-19 transmission: incubation period, reproduction rate, and multiple-generation spreading. Front. Phys. 2021;8
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
