The EZH2 selective inhibitor ZLD1039 attenuates UUO-induced renal fibrosis by suppressing YAP activation
- PMID: 40478495
- PMCID: PMC12144025
- DOI: 10.1186/s43556-025-00276-5
The EZH2 selective inhibitor ZLD1039 attenuates UUO-induced renal fibrosis by suppressing YAP activation
Abstract
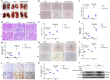
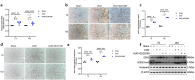
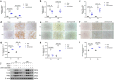
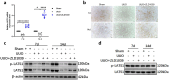
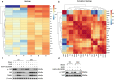
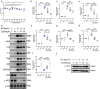
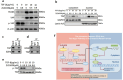
Renal fibrosis is a manifestation of the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and chronic inflammation is a main driver in the development of renal fibrosis. Yes-associated protein (YAP), acting as a transcriptional co-activator within the Hippo signaling pathway, has been implicated in renal fibrosis. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) exhibits high expression level in renal fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO), yet the interplay between YAP and EZH2 in renal fibrosis remains to be elucidated. ZLD1039, a selective inhibitor of EZH2, has demonstrated protective effects against cancer and acute kidney injury (AKI). In this study, we conducted a systemic pharmacological investigation to determine if ZLD1039 treatment mitigates UUO-induced renal inflammation and fibrosis through modulation of the Hippo-YAP pathway. Our results revealed that UUO triggered renal inflammation and collagen deposition, with significant activation of YAP. Notably, ZLD1039 treatment effectively alleviated renal inflammation and fibrosis, while inhibiting the expression and nuclear translocation of YAP. Mechanically, we observed a notable down-regulation of large tumor suppressor homolog 1 (LATS1) in parallel with the up-regulation of EZH2. Furthermore, inhibition of EZH2 by ZLD1039 was linked to the up-regulation of LATS1 expression and YAP inactivation. Similarly, in vitro pharmacological inhibition of EZH2 by ZLD1039 resulted in elevated LATS1 expression and diminished YAP activation. Collectively, our findings suggest that ZLD1039, a selective inhibitor of EZH2, likely attenuates renal inflammation and fibrosis probably by up-regulating LATS1 and inhibiting YAP activation. This mechanistic link between EZH2 and YAP provides a fresh perspective on treating renal fibrosis.
Keywords: Enhancer of zeste homolog 2; Inflammation; Large tumor suppressor 1; Renal fibrosis; Yes-associated protein 1.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The experimental scheme was approved by the Ethics Committee of Southwest Medical University (NO.20240715-008) and followed the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
