Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes mitigate acute radiation-induced intestinal oxidative damage via the Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 40478886
- PMCID: PMC12143498
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324238
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes mitigate acute radiation-induced intestinal oxidative damage via the Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 signaling pathway
Abstract
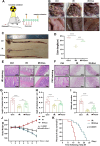
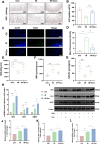
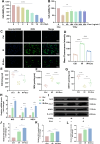
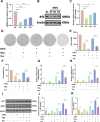
Acute radiation-induced intestinal injury (ARII), a prevalent complication of abdominal radiotherapy, remains clinically challenging due to limited therapeutic options. This study demonstrates the therapeutic efficacy of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (hucMSC-Exos) in mitigating ARII through Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 pathway activation. In a rat model receiving 12 Gy abdominal irradiation, systemic hucMSC-Exos administration significantly restored intestinal mucosal integrity and reduced oxidative damage markers. Mechanistically, hucMSC-Exos potentiated the antioxidant axis by upregulating Nrf2 signaling, as evidenced by histopathological, biochemical, and molecular analyses. Complementary in vitro experiments revealed hucMSC-Exos protected irradiated IEC-6 cells from oxidative dysfunction while enhancing proliferation, effects substantially attenuated upon Nrf2 silencing via siRNA. These findings establish that hucMSC-Exos orchestrate redox equilibrium through targeted Nrf2 pathway modulation, effectively counteracting radiation-induced enterocyte apoptosis. The elucidated mechanism expands the therapeutic paradigm of MSC-derived exosomes in radioprotection and provides a clinically translatable strategy for managing ARII in oncological radiotherapy.
Copyright: © 2025 Wang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
3D cultured human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell spheroids regulate oxidative stress and iron homeostasis through the Nrf2 pathway to resist ferroptosis in ovarian granulosa cells and ovarian dysfunction.Free Radic Biol Med. 2025 Aug 16;236:28-40. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2025.05.396. Epub 2025 May 16. Free Radic Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40383404
-
Polysaccharides extracted from Rheum tanguticum ameliorate radiation-induced enteritis via activation of Nrf2/HO-1.J Radiat Res. 2021 Jan 1;62(1):46-57. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rraa093. J Radiat Res. 2021. PMID: 33140083 Free PMC article.
-
Pyrogallol enhances therapeutic effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells against LPS-mediated inflammation and lung injury via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling.Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 Oct;191:66-81. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.08.030. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 36028178
-
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes act via the miR-1263/Mob1/Hippo signaling pathway to prevent apoptosis in disuse osteoporosis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Apr 16;524(4):883-889. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.001. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32057365
-
Exosomes released by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells protect against cisplatin-induced renal oxidative stress and apoptosis in vivo and in vitro.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013 Apr 25;4(2):34. doi: 10.1186/scrt194. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 23618405 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

