A multicenter cross-sectional study on factors associated with caregiving appraisal in pediatric acute leukemia caregivers
- PMID: 40478907
- PMCID: PMC12143579
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324589
A multicenter cross-sectional study on factors associated with caregiving appraisal in pediatric acute leukemia caregivers
Abstract
Introduction: Caring for pediatric acute leukemia (PAL) patients poses significant psychological challenges for family caregivers, impacting their well-being and caregiving capacity. This multicenter study aimed to assess caregivers' perception of their caregiving role using the revised Caregiving Appraisal Scale (rCAS) and identify factors associated with negative and positive caregiving appraisals among caregivers of children with PAL.
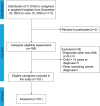
Methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted across three hospitals affiliated with Central South University. The 4-domain rCAS assessed both positive (satisfaction, mastery) and negative (burden, environmental impact) caregiving appraisals. Patient clinical data as well as demographics of both patients and caregivers were used to perform univariate, correlation, and multivariate regression analyses, identifying predictors of caregiver psychological distress.
Results: Out of 111 recruited caregivers, 101 valid responses were analyzed. Univariate subgroup analysis showed that several caregiver- and patient-related factors were significantly associated with increased caregiver burden and environmental impact. For mastery and satisfaction, some factors were associated with higher appraisal scores while others were related to significantly lower scores. Correlation analysis showed that patient discomfort and difficulties significantly correlated with both negative and positive appraisals. The regression models revealed that the independent influencing factors contributed to about 23.9% of caregiver-perceived negative impact (P = 0.024) and 30.3% of caregiver-perceived positive impact (P < 0.001). Patient worry (P = 0.024), communication difficulties (P = 0.011), relationship to the patient (P = 0.017), and medical insurance type (P = 0.035) predicted negative appraisals while pain (P = 0.008), anxiety about surgical procedures (P = 0.022), relationship to the patient (P = 0.031), and caregiver educational level (P = 0.023) predicted positive appraisals.
Conclusion: Caregivers of pediatric acute leukemia experience considerable psychological strain. Despite these challenges, some caregivers report significantly higher positive appraisals. Targeted interventions are needed to reduce caregiver burden and enhance positive caregiving outcomes.
Copyright: © 2025 Ouru et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determinant Factors of Stress in Caregivers of Patients With Schizophrenia: Cross-Sectional Study.JMIR Form Res. 2025 Jul 3;9:e70648. doi: 10.2196/70648. JMIR Form Res. 2025. PMID: 40608481 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Psychological Resilience and Self-Efficacy on Caregiver Burden: A Cross-Sectional Study Among Caregivers of People With Alzheimer's Disease.Nurs Open. 2025 Aug;12(8):e70288. doi: 10.1002/nop2.70288. Nurs Open. 2025. PMID: 40755264 Free PMC article.
-
How lived experiences of illness trajectories, burdens of treatment, and social inequalities shape service user and caregiver participation in health and social care: a theory-informed qualitative evidence synthesis.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025 Jun;13(24):1-120. doi: 10.3310/HGTQ8159. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025. PMID: 40548558
-
Factors that influence parents' and informal caregivers' views and practices regarding routine childhood vaccination: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 27;10(10):CD013265. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013265.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34706066 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between the quality of formal care and family caregivers' positive and negative aspects of caregiving for older patients with chronic conditions.Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2025 Jun;25(6):749-757. doi: 10.1111/ggi.70038. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2025. PMID: 40268872
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical