The SH protein of mumps virus is a druggable pentameric viroporin
- PMID: 40479045
- PMCID: PMC12143350
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ads3071
The SH protein of mumps virus is a druggable pentameric viroporin
Abstract
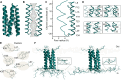
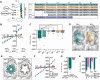
Viral infections are on the rise and drugs targeting viral proteins are needed. Viroporins constitute a growing group of virus-encoded transmembrane oligomeric proteins that allow passage of small molecules across the membrane. Despite sparsity in viroporin structures, recent work has revealed diversity in both the number of transmembrane helices and oligomeric states. Here, we provide evidence that the small hydrophobic protein (SH) from mumps virus is a pentameric viroporin. From extensive biophysical data, a HADDOCK model of full-length SH shows its intracellular C-terminal region to form an extended structure crucial to stabilization of the pentamer. Heterologous expression of wild-type SH and variants in Xenopus laevis oocytes reveals the viroporin as a chloride channel, with transport facilitated by conserved hydroxyl-carrying residues lining the pore. The channel function of SH is inhibited by the small-molecule BIT225, highlighting the potential for antiviral targeting through SH.
Figures



References
-
- Lau R. K., Turner M. D., Viral mumps: Increasing occurrences in the vaccinated population. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 128, 386–392 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Takeuchi K., Tanabayashi K., Hishiyama M., Yamada A., The mumps virus SH protein is a membrane protein and not essential for virus growth. Virology 225, 156–162 (1996). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

