Chemokines kill bacteria without triggering antimicrobial resistance by binding anionic phospholipids
- PMID: 40479071
- PMCID: PMC12143392
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ads2675
Chemokines kill bacteria without triggering antimicrobial resistance by binding anionic phospholipids
Abstract
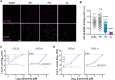
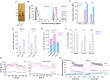
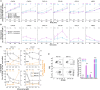
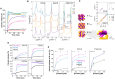
Classically, chemokines coordinate leukocyte trafficking; however, many chemokines also have direct antibacterial activity. The bacterial killing mechanism of chemokines and the biochemical properties that define which members of the chemokine superfamily are antimicrobial remain poorly understood. We report that the antimicrobial activity of chemokines is defined by their ability to bind phosphatidylglycerol and cardiolipin, two anionic phospholipids commonly found in the bacterial plasma membrane. We show that only chemokines able to bind these two phospholipids kill bacteria and that they exert rapid bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects with a higher potency than the antimicrobial peptide β-defensin 3. Both biochemical and genetic interference with the chemokine-cardiolipin interaction impaired microbial growth arrest, bacterial killing, and membrane disruption by chemokines. Moreover, unlike conventional antibiotics, Escherichia coli failed to develop resistance when placed under increasing antimicrobial chemokine pressure in vitro. Thus, we have identified cardiolipin and phosphatidylglycerol as binding partners for chemokines responsible for chemokine antimicrobial action.
Figures


Update of
-
Chemokines Kill Bacteria by Binding Anionic Phospholipids without Triggering Antimicrobial Resistance.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 25:2024.07.25.604863. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.25.604863. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Sci Adv. 2025 Jun 6;11(23):eads2675. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ads2675. PMID: 39091850 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Cassini A., Högberg L. D., Plachouras D., Quattrocchi A., Hoxha A., Simonsen G. S., Colomb-Cotinat M., Kretzschmar M. E., Devleesschauwer B., Cecchini M., Ouakrim D. A., Oliveira T. C., Struelens M. J., Suetens C., Monnet D. L., Strauss R., Mertens K., Struyf T., Catry B., Latour K., Ivanov I. N., Dobreva E. G., Tambic Andraševic A., Soprek S., Budimir A., Paphitou N., Žemlicková H., Schytte Olsen S., Wolff Sönksen U., Märtin P., Ivanova M., Lyytikäinen O., Jalava J., Coignard B., Eckmanns T., Abu Sin M., Haller S., Daikos G. L., Gikas A., Tsiodras S., Kontopidou F., Tóth Á., Hajdu Á., Guólaugsson Ó., Kristinsson K. G., Murchan S., Burns K., Pezzotti P., Gagliotti C., Dumpis U., Liuimiene A., Perrin M., Borg M. A., de Greeff S. C., Monen J. C. M., Koek M. B. G., Elstrøm P., Zabicka D., Deptula A., Hryniewicz W., Caniça M., Nogueira P. J., Fernandes P. A., Manageiro V., Popescu G. A., Serban R. I., Schréterová E., Litvová S., Štefkovicová M., Kolman J., Klavs I., Korošec A., Aracil B., Asensio A., Pérez-Vázquez M., Billström H., Larsson S., Reilly J. S., Johnson A., Hopkins S., Burden of AMR Collaborative Group , Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: A population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 19, 56–66 (2019). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

