Sativex (nabiximols) for the treatment of Agitation & Aggression in Alzheimer's dementia in UK nursing homes: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled feasibility trial
- PMID: 40479610
- PMCID: PMC12143470
- DOI: 10.1093/ageing/afaf149
Sativex (nabiximols) for the treatment of Agitation & Aggression in Alzheimer's dementia in UK nursing homes: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled feasibility trial
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's Disease (ad) patients often experience clinically significant agitation, leading to distress, increased healthcare costs and earlier institutionalisation. Current treatments have limited efficacy and significant side effects. Cannabinoid-based therapies, such as the nabiximols oral spray (Sativex®; 1:1 delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol), offer potential alternatives. We aimed to explore the feasibility and safety of nabiximols as a potential treatment for agitation in ad.
Methods: The 'Sativex® for Agitation & Aggression in Alzheimer's Dementia' (STAND) trial was a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, feasibility study conducted in UK care homes. Participants with probable ad and predefined clinically significant agitation were randomised to receive placebo or nabiximols for 4 weeks on an up-titrated schedule, followed by a 4-week observation period. To be considered feasible, we prespecified the following thresholds that needed to be met: randomising 60 participants within 12 months, achieving a ≥ 75% follow-up rate at 4 weeks, maintaining ≥80% adherence to allocation and estimating a minimum effect size (Cohen's d ≥ 0.3) on the Cohen-Mansfield Agitation Inventory. This trial is registered with ISRCTN 7163562.
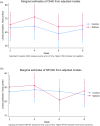
Findings: Between October 2021 and June 2022, 53 candidates were assessed; 29 met eligibility criteria and were randomised. No participants withdrew, and adherence was high (100%) and was generally feasible to deliver. The intervention was well tolerated (0 adverse reactions), with no safety concerns reported.
Interpretation: Despite significant COVID-19 pandemic related challenges, administering nabiximols through oral mucosa to advanced ad patients with agitation demonstrated feasibility and safety. These findings support a larger confirmatory efficacy trial to evaluate the potential therapeutic efficacy of nabiximols for agitation in ad.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; behavioural and psychological symptoms of dementia; cannabinoid-based medicine; dementia; neuropsychiatric symptoms; older people.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Geriatrics Society.
Conflict of interest statement
T.W.G. is/has been supported by the grants from the Taiwanese Ministry of Education, the National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan, the Elite Physician fund, China Medical University Beigang Hospital, Taiwan, the Alzheimer’s Association, US and the Alzheimer’s Research UK. L.V. is/has been supported by grants from the NIHR, UK; Psychiatry Research trust; Parkinson’s UK; Rosetrees Trust; Alzheimer’s Research UK. S.B. is/has been supported by grants from the NIHR, UK; Wellcome trust; Psychiatry Research trust; Parkinson’s UK; Rosetrees Trust; Alzheimer’s Research UK. S.B. has participated in advisory boards for or received research funding from EmpowerPharm/SanteCannabis and NW PharmaTech Ltd. All of these honoraria/funding were received as contributions towards research support through King’s College London and not personally. S.B. also had a collaboration with Beckley Canopy Therapeutics/Canopy Growth (investigator-initiated research) wherein they supplied study drug for free for charity (Parkinson’s UK) and NIHR (BRC) funded research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Algorithm-based pain management for people with dementia in nursing homes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 1;4(4):CD013339. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013339.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35363380 Free PMC article.
-
Donepezil for dementia due to Alzheimer's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 18;6(6):CD001190. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001190.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29923184 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacotherapies for sleep disturbances in dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 16;11(11):CD009178. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009178.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 15;11:CD009178. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009178.pub4. PMID: 27851868 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Selegiline for Alzheimer's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(1):CD000442. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000442. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. PMID: 12535396
-
Efficacy of Add-On Agomelatine on Agitation, Aggression, and Neuroprotection in Alzheimer's Disease: A Randomized, Blinded, Controlled Trial.Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2025 Aug;33(8):819-834. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2025.03.001. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40221303 Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous