Phase III Trial of Pirtobrutinib Versus Idelalisib/Rituximab or Bendamustine/Rituximab in Covalent Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Pretreated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (BRUIN CLL-321)
- PMID: 40479620
- PMCID: PMC12288890
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO-25-00166
Phase III Trial of Pirtobrutinib Versus Idelalisib/Rituximab or Bendamustine/Rituximab in Covalent Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Pretreated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (BRUIN CLL-321)
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Phase III Trial of Pirtobrutinib Versus Idelalisib/Rituximab or Bendamustine/Rituximab in Covalent Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Pretreated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (BRUIN CLL-321).J Clin Oncol. 2025 Aug 10;43(23):2658. doi: 10.1200/JCO-25-01356. Epub 2025 Jun 27. J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40577663 No abstract available.
-
Erratum: Phase III Trial of Pirtobrutinib Versus Idelalisib/Rituximab or Bendamustine/Rituximab in Covalent Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Pretreated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (BRUIN CLL-321).J Clin Oncol. 2025 Sep;43(25):2841. doi: 10.1200/JCO-25-01700. Epub 2025 Jul 29. J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40729625 No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: Pirtobrutinib, a noncovalent, Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi), has shown clinical efficacy and a favorable safety profile. BRUIN CLL-321 was an open-label, randomized phase III study conducted exclusively in patients with R/R chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) previously treated with cBTKi, and compared pirtobrutinib with investigator's choice (IC) of idelalisib/rituximab (IdelaR) or bendamustine/rituximab (BR).
Methods: Patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive pirtobrutinib (200 mg once daily) or IC of IdelaR or BR, and were stratified by previous use of venetoclax and del(17p). The primary end point was independent review committee-assessed progression-free survival (PFS). Secondary end points included time to next treatment or death (TTNT), overall survival (OS), and safety. The primary PFS end point was met at the time of the primary analysis (August 29, 2023), and updated results are reported from the final OS analysis (August 29, 2024).
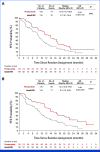
Results: A total of 238 patients were randomly assigned to receive pirtobrutinib (n = 119) or IC (n = 119; IdelaR [n = 82], BR [n = 37]). The PFS hazard ratio (HR) was 0.54 ([95% CI, 0.39 to 0.75]; P = .0002), with a median PFS of 14 months (95% CI, 11.2 to 16.6) in the pirtobrutinib group and 8.7 months (95% CI, 8.1 to 10.4) with IC. The unadjusted OS HR was 1.09 ([95% CI, 0.68 to 1.75]; P = .7202), and 18-month OS rate was 73.4% (95% CI, 63.9 to 80.7) in the pirtobrutinib group and 70.8% (95% CI, 60.9 to 78.7) with IC. Median TTNT was 24 months (95% CI, 17.8 to 29.7) with pirtobrutinib versus 10.9 months (95% CI, 8.7 to 12.5) with IC (HR, 0.37 [95% CI, 0.25 to 0.52]). At a median follow-up of 17.2 months, grade ≥3 treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) were lower with pirtobrutinib (57.7%) than IC (73.4%). Treatment discontinuation due to AE occurred in 20 (17.2%) patients receiving pirtobrutinib and 38 (34.9%) patients receiving IC.
Conclusion: Pirtobrutinib improved PFS and TTNT, and demonstrated favorable tolerability, versus IdelaR/BR in exclusively cBTKi pretreated patients with CLL/SLL.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04666038.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures



References
-
- Wierda WG, Brown J, Abramson JS, et al. : NCCN Guidelines® insights: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma, version 3.2022. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 20:622-634, 2022 - PubMed
-
- Smith TW, Owusu HF, Wormser D, et al. : Real-world evaluation of the treatment landscape for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 138:1559, 2021
-
- Ysebaert L, Ferrant E, Dilhuydy MS, et al. : Outcomes of CLL patients exposed to venetoclax+/-R after ibrutinib in France: The resist retrospective study from the Filo-CLL Group. Blood 142:3273, 2023
-
- Samples L, Khajaviyan S, Lynch RC, et al. : Predictors of outcomes with venetoclax-based treatment in patients with progressive disease or intolerance after covalent BTK inhibitors. Blood 142:4656, 2023
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

