Mazdutide, a dual agonist targeting GLP-1R and GCGR, mitigates diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction: mechanistic insights from multi-omics analysis
- PMID: 40479843
- PMCID: PMC12205698
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105791
Mazdutide, a dual agonist targeting GLP-1R and GCGR, mitigates diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction: mechanistic insights from multi-omics analysis
Abstract
Background: Cognitive impairment and dementia are highly associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Recent studies have demonstrated that GLP-1 receptor agonists can improve cognitive function through brain activation in patients with T2DM, compared to other oral glucose-lowering drugs. Mazdutide, a dual agonist of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) and the glucagon receptor (GCGR), has been shown to simultaneously reduce body weight, blood glucose levels, and other comorbidities associated with obesity in patients with T2DM. While its insulinotropic and glucose-lowering effects through the GLP-1 pathway are well-established, mazdutide may also enhance energy expenditure via activation of the GCGR pathway. However, its potential impact on cognitive function remains to be elucidated.
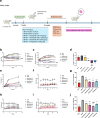
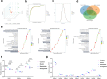
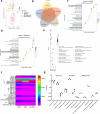
Methods: This study aimed to investigate the effects of mazdutide on cognitive behaviour and cerebral pathology in male db/db mice, a model of T2DM, in comparison to dulaglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist. All animal findings are applicable to male mice only. Behavioural tests were conducted to evaluate cognitive function, and pathological analyses were performed to assess neurodegenerative markers in the brain. Furthermore, transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomics analyses were employed to explore the underlying molecular mechanisms of mazdutide's effects.
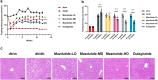
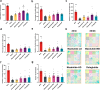
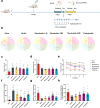
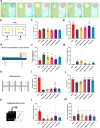
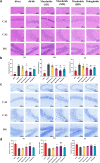
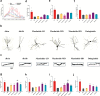
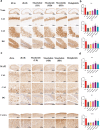
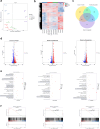
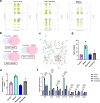
Findings: Compared to dulaglutide, mazdutide significantly improved cognitive performance in db/db mice, as evidenced by comprehensive behavioural tests. Pathological assessments revealed improvements in neuronal structure and brain tissue integrity in the mazdutide-treated group. Multi-omics analyses further identified distinct molecular pathways involved in neuroprotection, energy metabolism, and synaptic plasticity, suggesting that dual GLP-1/GCGR activation contributes to enhanced cognitive resilience.
Interpretation: Our findings indicate that mazdutide, via its dual GLP-1/GCGR activation effects, exerts multifactorial improvements in cognitive function in the context of obesity and T2DM. These results suggest that mazdutide is a promising therapeutic option for mitigating cognitive deficits associated with metabolic disorders.
Funding: Medical Science and Technology Research and Development Plan Major Project Jointly Constructed by the Henan Province and Ministerial Departments in China (No. SBGJ202301010).
Keywords: Diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction; GLP-1R/GCGR dual agonism; Mazdutide; db/db mice.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests Innovent Biologics, Inc. provided Mazdutide for use in this study. The authors declare no other competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tirzepatide mitigates cognitive decline in zebrafish model of type 2 diabetes mellitus induced by high-fat diet.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):8861-8883. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03827-3. Epub 2025 Jan 28. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39873719
-
Dipeptidyl-peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 analogues for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in people at increased risk for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 10;5(5):CD012204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012204.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28489279 Free PMC article.
-
Tirzepatide, a dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide/glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist, exhibits favourable effects on pancreatic β-cells and hepatic steatosis in obese type 2 diabetic db/db mice.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024 Dec;26(12):5982-5994. doi: 10.1111/dom.15972. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024. PMID: 39344853
-
Seven glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and polyagonists for weight loss in patients with obesity or overweight: an updated systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Metabolism. 2024 Dec;161:156038. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2024.156038. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Metabolism. 2024. PMID: 39305981
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists compared with basal insulins for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017 Feb;19(2):228-238. doi: 10.1111/dom.12805. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017. PMID: 27717130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen S., Kuper H. Tracing the temporal trends of modifiable risk factors in dementia: insights from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing (2004–2019) Lancet. 2023;402(Suppl 1):S34. - PubMed
-
- Ninomiya T. Diabetes mellitus and dementia. Curr Diab Rep. 2014;14:487. - PubMed
-
- Luo A., Xie Z., Wang Y., et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus-associated cognitive dysfunction: advances in potential mechanisms and therapies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022;137 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

