tsRNA-08614 inhibits glycolysis and histone lactylation by ALDH1A3 to confer oxaliplatin sensitivity in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 40480147
- PMCID: PMC12169791
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2025.102427
tsRNA-08614 inhibits glycolysis and histone lactylation by ALDH1A3 to confer oxaliplatin sensitivity in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: Enhanced glycolysis contributes to the chemotherapy resistance of colorectal cancer (CRC). However, whether tRNA-derived small RNAs (tsRNAs) regulate CRC oxaliplatin sensitivity through glycolysis-mediated histone lactylation remains unclear.
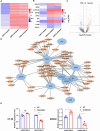
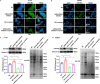
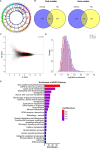
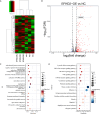
Methods: By analyzing RNA-seq data from CRC samples in the TCGA database, we identified a glucose metabolism-related tsRNA. Overexpression of tsRNA-08614 was investigated to explore its impact on CRC sensitivity to oxaliplatin. The targeting gene of tsRNA-08614 was validated through a dual-luciferase reporter assay. The specific molecular mechanism of tsRNA-08614 regulating CRC oxaliplatin sensitivity was further revealed by ChIP-seq and RNA-seq.
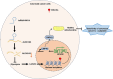
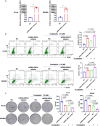
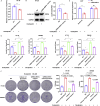
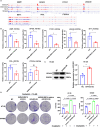
Results: We found a down-regulated tsRNA-08614 targeted glycolysis-related gene, which was associated with chemotherapy resistance. Overexpression of tsRNA-08614 promoted oxaliplatin sensitivity of CRC cells. tsRNA-08614 inhibited the expression of the target gene ALDH1A3 and reduced glycolysis, whereas the glycolytic inducer reversed the enhanced sensitivity caused by tsRNA-08614. Interference of tsRNA-08614 increased H3K18la and pan-Kla levels, while the lactate inhibitor partially suppressed these effects. Furthermore, overexpression of tsRNA-08614 reprogrammed the transcription of genes mediated by histone lactylation modification, with EFHD2 showing the most significant differential expression. EFHD2 inhibited the sensitivity of CRC cells to oxaliplatin by upregulating CMPK2 and enhancing mitochondrial function. Finally, we demonstrated that tsRNA-08614 enhanced sensitivity to oxaliplatin in CRC by reducing histone lactylation levels in vivo.
Conclusion: tsRNA-08614 regulates ALDH1A3 to inhibit glycolysis and histone lactylation modification, thereby suppressing the transcriptional activity of EFHD2 and ultimately promoting the sensitivity of CRC to oxaliplatin. These findings suggest that tsRNA-08614 may represent a novel molecular target to combat oxaliplatin resistance in CRC chemotherapy.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Glycolysis; Histone lactylation; tsRNA.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The LncRNA STEAP3-AS1 promotes liver metastasis in colorectal cancer by regulating histone lactylation through chromatin remodelling.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Jul 15;44(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03461-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40665344 Free PMC article.
-
Histone lactylation-driven YTHDF2 promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell glycolysis and stemness by recognizing m6A modification of SFRP2.Biochem Pharmacol. 2025 Oct;240:117097. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2025.117097. Epub 2025 Jul 4. Biochem Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40619016
-
Cancer associated fibroblasts-derived lactate induces oxaliplatin treatment resistance by promoting cancer stemness via ANTXR1 lactylation in colorectal cancer.Cancer Lett. 2025 Jul 17;631:217917. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217917. Online ahead of print. Cancer Lett. 2025. PMID: 40683418
-
Glucose Metabolism, Lactate, Lactylation and Alzheimer's Disease.Aging Dis. 2025 Jun 25. doi: 10.14336/AD.2025.0338. Online ahead of print. Aging Dis. 2025. PMID: 40586382 Review.
-
tsRNA modifications: An emerging layer of biological regulation in disease.J Adv Res. 2025 Aug;74:403-414. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.09.010. Epub 2024 Sep 10. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 39260796 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

