Efficacy of a 6-month supported online programme (Feeling Safer) for the treatment of persecutory delusions: protocol for a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 40480660
- PMCID: PMC12161337
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2025-104580
Efficacy of a 6-month supported online programme (Feeling Safer) for the treatment of persecutory delusions: protocol for a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Introduction: Persecutory delusions are very common in severe mental health disorders such as schizophrenia. Existing treatments often do not work well enough. We developed a face-to-face theory-driven psychological intervention, called Feeling Safe, that produces very large reductions in persistent persecutory delusions. The challenge now is to make Feeling Safe widely available. So, we developed a 6-month supported online version, called Feeling Safer. The aim is an intervention that patients can easily access and use, reduces persecutory delusions and can be supported by a range of mental health professionals in less contact time than face-to-face therapy. Initial proof of concept testing of Feeling Safer was very encouraging. In a randomised controlled trial, we now plan to test whether Feeling Safer is efficacious for patients and can be successfully delivered by any of three different mental health staff groups (peer-support workers, graduate psychologists and cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) therapists). We will also test whether Feeling Safer works equally across gender, age, ethnicity and cognitive functioning (moderation) and whether Feeling Safer works via the targeted psychological processes (mediation).
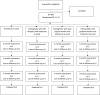
Methods and analysis: The study design is a multicentre, single-blind (outcome assessor), parallel, four-arm randomised controlled trial; 484 patients with persistent persecutory delusions will be randomised to one of the four conditions (1:1:1:1): Feeling Safer (added to treatment as usual (TAU)) supported by peer-support workers, or Feeling Safer (added to TAU) supported by graduate mental health workers including assistant psychologists, or Feeling Safer (added to TAU) supported by CBT therapists or TAU. Feeling Safer will be provided for 6 months with a staff member. Assessments will be conducted at 0, 3, 6 and 9 months by research assistants blind to group allocation. The primary outcome is severity of persecutory delusions at 6 months rated with the Psychotic Symptoms Rating Scale-Delusions. The secondary outcomes are other psychiatric symptoms (depression, anxiety, insomnia, agoraphobia and paranoia), psychological well-being, recovery, activity and health-related quality of life. Analysis will be conducted under a treatment policy strategy following the intention-to-treat principle, incorporating data from all participants including those who do not complete treatment. Moderation and mediation will be tested. A within-trial cost-effectiveness analysis will be conducted of Feeling Safer compared with TAU.
Ethics and dissemination: The trial has received ethical approval from the NHS Health Research Authority (23/LO/0951). Informed consent will be obtained from all participants. A key output will be an open-access publication in a peer-reviewed journal reporting on the clinical effectiveness of a high-quality supported online programme for the treatment of persecutory delusions that has the potential to be used at scale in mental health services.
Trial registration number: ISRCTN93974770.
Keywords: Adult psychiatry; Digital Technology; MENTAL HEALTH; Randomized Controlled Trial; Schizophrenia & psychotic disorders.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A 6-month supported online program for the treatment of persecutory delusions: Feeling Safer.Psychol Med. 2025 Jun 30;55:e179. doi: 10.1017/S0033291725100676. Psychol Med. 2025. PMID: 40583552 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Automated virtual reality cognitive therapy versus virtual reality mental relaxation therapy for the treatment of persistent persecutory delusions in patients with psychosis (THRIVE): a parallel-group, single-blind, randomised controlled trial in England with mediation analyses.Lancet Psychiatry. 2023 Nov;10(11):836-847. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(23)00257-2. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Lancet Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37742702 Free PMC article.
-
E-Health interventions for anxiety and depression in children and adolescents with long-term physical conditions.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 15;8(8):CD012489. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012489.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30110718 Free PMC article.
-
Therapist-supported Internet cognitive behavioural therapy for anxiety disorders in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 12;3(3):CD011565. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011565.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26968204 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A 6-month supported online program for the treatment of persecutory delusions: Feeling Safer.Psychol Med. 2025 Jun 30;55:e179. doi: 10.1017/S0033291725100676. Psychol Med. 2025. PMID: 40583552 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical