Inconsistency of AI in intracranial aneurysm detection with varying dose and image reconstruction
- PMID: 40481138
- PMCID: PMC12144221
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-04830-7
Inconsistency of AI in intracranial aneurysm detection with varying dose and image reconstruction
Abstract
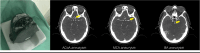
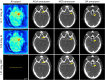
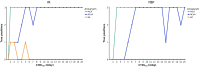
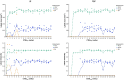
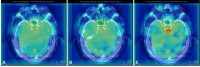
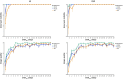
Scanner-related changes in data quality are common in medical imaging, yet monitoring their impact on diagnostic AI performance remains challenging. In this study, we performed standardized consistency testing of an FDA-cleared and CE-marked AI for triage and notification of intracranial aneurysms across changes in image data quality caused by dose and image reconstruction. Our assessment was based on repeated examinations of a head CT phantom designed for AI evaluation, replicating a patient with three intracranial aneurysms in the anterior, middle and posterior circulation. We show that the AI maintains stable performance within the medium dose range but produces inconsistent results at reduced dose and, unexpectedly, at higher dose when filtered back projection is used. Data quality standards required for AI are stricter than those for neuroradiologists, who report higher aneurysm visibility rates and experience performance degradation only at substantially lower doses, with no decline at higher doses.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Computed tomography angiography; Imaging phantoms; Intracranial aneurysm; Reproducibility of findings.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: Bernd Hamm is shareholder, Michael Scheel is patent inventor and shareholder, and Paul Jahnke is patent inventor, shareholder, and part-time employee of PhantomX GmbH. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dual-energy CT angiography in the evaluation of intracranial aneurysms: image quality, radiation dose, and comparison with 3D rotational digital subtraction angiography.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010 Jan;194(1):23-30. doi: 10.2214/AJR.08.2290. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010. PMID: 20028901
-
Assessing the Impact of an Artificial Intelligence-Based Model for Intracranial Aneurysm Detection in CT Angiography on Patient Diagnosis and Outcomes (IDEAL Study)-a protocol for a multicenter, double-blinded randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2024 Jun 4;25(1):358. doi: 10.1186/s13063-024-08184-9. Trials. 2024. PMID: 38835091 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence can help detecting incidental intracranial aneurysm on routine brain MRI using TOF MRA data sets and improve the time required for analysis of these images.Neuroradiology. 2024 Dec;66(12):2195-2204. doi: 10.1007/s00234-024-03460-6. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Neuroradiology. 2024. PMID: 39230716
-
Complex Relationship Between Artificial Intelligence and CT Radiation Dose.Acad Radiol. 2022 Nov;29(11):1709-1719. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2021.10.024. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Acad Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34836775 Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence Applications in Intracranial Aneurysm: Achievements, Challenges and Opportunities.Acad Radiol. 2022 Mar;29 Suppl 3:S201-S214. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2021.06.013. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Acad Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34376335 Review.
References
-
- Rinkel, G. J., Djibuti, M., Algra, A. & van Gijn, J. Prevalence and risk of rupture of intracranial aneurysms: A systematic review. Stroke29, 251–256. 10.1161/01.str.29.1.251 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Vlak, M. H., Algra, A., Brandenburg, R. & Rinkel, G. J. Prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms, with emphasis on sex, age, comorbidity, country, and time period: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol.10, 626–636. 10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70109-0 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Vernooij, M. W. et al. Incidental findings on brain MRI in the general population. N Engl. J. Med.357, 1821–1828. 10.1056/NEJMoa070972 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Westerlaan, H. E. et al. Intracranial aneurysms in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage: CT angiography as a primary examination tool for diagnosis–systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiology258, 134–145. 10.1148/radiol.10092373 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Yoon, N. K., McNally, S., Taussky, P. & Park, M. S. Imaging of cerebral aneurysms: A clinical perspective. Neurovascular Imaging2, 6. 10.1186/s40809-016-0016-3 (2016).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

