Identifying factors related to sertraline concentrations in child/adolescent and adult patients: insights from a therapeutic drug monitoring service
- PMID: 40481507
- PMCID: PMC12142871
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-025-07033-6
Identifying factors related to sertraline concentrations in child/adolescent and adult patients: insights from a therapeutic drug monitoring service
Abstract
Introduction: Sertraline, a widely prescribed antidepressant, has considerable variability in serum concentrations. This retrospective study aimed to identify key determinants influencing sertraline concentrations, with a special focus on age-related differences.
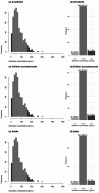
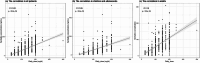
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of TDM data from 1076 patients (474 children/adolescents and 602 adults) collected between 2018 and 2024. Multivariable generalized linear regression and restricted cubic spline models were used to examine the relationships between clinical parameters and sertraline concentrations.
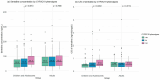
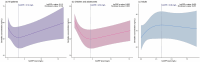
Results: The daily dose and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) level were positively correlated with the sertraline concentration in both age groups. Sex had a significant effect, with women exhibiting 43% (P = 0.001) and 37% (P = 0.001) higher concentrations than men in the child/adolescent and adult groups, respectively. In children and adolescents, the albumin (Alb) level and neutrophil (NEUT) count also considerably influence concentrations. CYP2C19 poor metabolizers (PMs) tended to be present at relatively high concentrations, but the difference was not statistically significant. Among child and adolescent patients, significant differences in dose-adjusted serum concentration (C/D) values (P = 0.0291) were observed across different CYP2C19 phenotypes, with PMs exhibiting higher C/D values. In a cohort of 593 patients who underwent high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) testing, a nonlinear, U-shaped correlation between hsCRP levels and sertraline concentrations was identified in children and adolescents.
Discussion: By identifying key factors such as daily dose, sex and AST levels, clinicians can develop tailored treatment plans for individual patients. These findings underscore the need for further research to elucidate the interplay between sertraline metabolism and patients' physiological and pathological characteristics.
Keywords: Antidepressants; Pharmacogenomics; Psychopharmacology; Therapeutic drug monitoring.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study, conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and with waived informed consent, was approved by the Ethics Committee of The Second People’s Hospital of Guizhou Province in China [(2024) Research No. 03]. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Consent to participate: Given that this study was a retrospective study utilizing data from electronic medical records, the Ethics Committee granted a waiver of informed consent, as the study posed no additional risk to participants. Clinical trial number: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Solmi M, et al. Safety of 80 antidepressants, antipsychotics, anti-attention-deficit/hyperactivity medications and mood stabilizers in children and adolescents with psychiatric disorders: a large scale systematic meta-review of 78 adverse effects. World Psychiatry. 2020;19(2):214–32. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

