The effect of radiotherapy on patients with EGFR-driven lung cancer brain metastasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40481965
- PMCID: PMC12145404
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-02780-0
The effect of radiotherapy on patients with EGFR-driven lung cancer brain metastasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
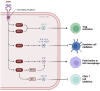
Background: Brain metastases (BMs) are a common and fatal consequence in patients with advanced malignancies. Mutations happening in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) are associated with an elevated risk BMs, occurring in approximately 20-40% of patients. This study evaluates the safety and efficacy of different radiotherapy (RT) modalities in patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancer brain metastases.
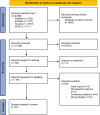
Method: This study was conducted according to the PRISMA guideline. A comprehensive search was conducted on PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Scopus, until 13 March 2024. Stata v.17 was used for statistical analysis.
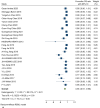
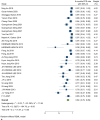
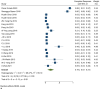
Result: A total of 57 studies involving 4614 patients were analyzed, with a female predominance of 59.55% and a mean age of 50-70 years. The 6-month overall survival (OS) rate was 94% [95% CI 91-96%], 81% [95% CI 78- 84%] at 1-year, 55% [95% CI 50-60%] at 2-year, 37% [95% CI 32-42%] at 3-year, decreasing to 21% [95% CI 16-26%] at 5 years. Progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 84% [95% CI 79-89%] at 6 months and 20% [95% CI 14-26%] at 3 years. Meta-regression analysis indicated that a higher number of metastases, Karnofsky performance status below 80, and an ECOG score over one were significantly linked to OS outcomes.
Conclusion: RT significantly improves survival outcomes in patients with EGFR-mutant brain metastases. However, the combination of RT with targeted therapies, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), appears to offer more favorable outcomes.
Keywords: Brain metastases; EGFR mutations; Non-small cell lung cancer; Radiotherapy; Stereotactic.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study is deemed to exempt to receive ethical approval. Consent to participate: Not applicable. Human ethics and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures












Similar articles
-
First-line treatment with TKI plus brain radiotherapy versus TKI alone in EGFR-mutated non-small cell Lung cancer with brain metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2023 Oct 30;23(1):1043. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11548-0. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37904083 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of EGFR-TKIs combined with intracranial radiotherapy in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: a retrospective multi-institutional analysis.Radiat Oncol. 2025 Jan 9;20(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13014-024-02578-4. Radiat Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39789554 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation (EGFR) Testing for Prediction of Response to EGFR-Targeting Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI) Drugs in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An Evidence-Based Analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010;10(24):1-48. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010. PMID: 23074402 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Combined with Cranial Radiotherapy for Brain Metastases from Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Protocol for a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 13;2022:6531748. doi: 10.1155/2022/6531748. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35872868 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of EGFR-TKI combined with WBRT vs. WBRT alone in the treatment of brain metastases from NSCLC: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Apr 26;15:1362061. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1362061. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38737351 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association between high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and diabetic nephropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Jul 26;26(1):418. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04358-y. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40713563 Free PMC article.
-
Association of CALLY index with NAFLD in U.S. adults from NHANES 2017-2020 assessed by vibration-controlled transient elastography.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025 Aug 29;17(1):363. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01926-y. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025. PMID: 40883838 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of probiotic supplementation on serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor: GRADE-based dose-response meta-analysis.BMC Nutr. 2025 Aug 11;11(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s40795-025-01152-9. BMC Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40790243 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Santarelli JG, et al. Molecular events of brain metastasis. Neurosurg Focus. 2007;22(3):E1. - PubMed
-
- Barnholtz-Sloan JS, et al. Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the metropolitan Detroit cancer surveillance system. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(14):2865–72. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
