Increased susceptibility to prostate cancer biomarkers in the offspring of male mouse progenitors with lifelong or early life exposure to high-fat diet
- PMID: 40481981
- PMCID: PMC12145303
- DOI: 10.1007/s00394-025-03737-3
Increased susceptibility to prostate cancer biomarkers in the offspring of male mouse progenitors with lifelong or early life exposure to high-fat diet
Abstract
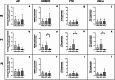
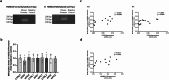
Obesity exacerbates hormonal dysregulation, inflammation, and oxidative stress, factors associated with Prostate Cancer (PCa) development. The (epi)genetic influences of obesity may be transgenerationally transmitted, potentially impacting PCa susceptibility in the offspring of fathers with obesity. Thus, we studied the impact of early-life or lifelong exposure to a high-fat diet (HFD) on PCa biomarkers [Homeobox B13 (HOXB13) and the Androgen Receptor (AR)] and their correlation with obesity-related markers. Furthermore, we focused on the offspring's PCa biomarkers outcomes and explored their potential link with paternal diet. A transgenerational Mus musculus model was established, with F0 males exposed to different diets (200 days): standard chow, lifelong HFD (HFD), and transient diet (60 days HFD, plus 140 days of standard chow) (HFDt). AR expression in the prostates was unaffected, whereas HOXB13, Fat Mass and Obesity Associated gene (FTO), and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-α) expression decreased in the F1 HFDt group. HOXB13 and AR prostate expression were positively correlated. There was also a positive correlation between FTO prostate expression and PCa biomarkers, and between TNF-α expression and FTO and PCa biomarkers. HOXB13 promoter methylation levels were unaffected, however, were positively correlated with FTO and HOXB13 expression. Finally, protein nitration remained unchanged in the prostates, while lipid peroxidation was increased in the F0 HFD group and decreased in the F1 and F2 HFD and HFDt groups. Our study highlights the intergenerational interplay between obesity-related factors and PCa biomarkers, suggesting that offspring of male progenitors subjected to HFD may face an increased risk for elevated PCa biomarkers expression.
Keywords: Epigenetic; Obesity; Prostate cancer; Transgenerational.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: The protocol of this study is compliant with the ARRIVE guidelines and was approved and licensed by the Portuguese Veterinarian and Food Department (DGAV) (0421/000/000/2016). Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

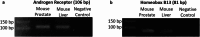
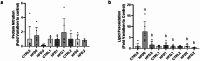
References
-
- Organization WH (2000) Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser, 2000. 894: pi-xii, 1-253 - PubMed
-
- Fock KM, Khoo J (2013) Diet and exercise in management of obesity and overweight. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 28(Suppl 4):59–63 - PubMed
-
- Chooi YC, Ding C, Magkos F (2019) The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism 92:6–10 - PubMed
-
- World Obesity A (2023) 2023, World Obesity Federation, London, UK, 2023 https://data.worldobesity.org/publications/?cat=19
-
- Wright SM, Aronne LJ (2012) Causes of obesity. Abdom Imaging 37(5):730–732 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

