Insulin- and exercise-induced phosphoproteomics of human skeletal muscle identify REPS1 as a regulator of muscle glucose uptake
- PMID: 40482643
- PMCID: PMC12208332
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102163
Insulin- and exercise-induced phosphoproteomics of human skeletal muscle identify REPS1 as a regulator of muscle glucose uptake
Abstract
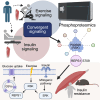
Skeletal muscle glucose uptake, essential for metabolic health, is regulated by both insulin and exercise. Using phosphoproteomics, we analyze skeletal muscle from healthy individuals following acute exercise or insulin stimulation, generating a valuable dataset. We identify 71 phosphosites on 55 proteins regulated by both stimuli in the same direction, suggesting a convergence of exercise and insulin signaling pathways. Among these, the vesicle-associated protein, REPS1, is highly phosphorylated at Ser709 in response to both stimuli. We identify p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) to be a key upstream kinase of REPS1 S709 phosphorylation and that the RSK-REPS1 signaling axis is involved in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake. Insulin-induced REPS1 Ser709 phosphorylation is closely linked to muscle and whole-body insulin sensitivity and is impaired in insulin-resistant mice and humans. These findings highlight REPS1 as a convergence point for insulin and exercise signaling, presenting a potential therapeutic target for treating individuals with insulin resistance.
Keywords: REPS1; RSK; exercise; glucose metabolism; insulin; phosphoproteomics; skeletal muscle signaling.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- DeFronzo R.A., Jacot E., Jequier E., Maeder E., Wahren J., Felber J.P. The Effect of Insulin on the Disposal of Intravenous Glucose: Results from Indirect Calorimetry and Hepatic and Femoral Venous Catheterization. Diabetes. 1981;30:1000–1007. - PubMed
-
- McConell G.K., Sjøberg K.A., Ceutz F., Gliemann L., Nyberg M., Hellsten Y., Frøsig C., Kiens B., Wojtaszewski J.F.P., Richter E.A. Insulin-induced membrane permeability to glucose in human muscles at rest and following exercise. J. Physiol. 2020;598:303–315. - PubMed
-
- Zisman A., Peroni O.D., Abel E.D., Michael M.D., Mauvais-Jarvis F., Lowell B.B., Wojtaszewski J.F., Hirshman M.F., Virkamaki A., Goodyear L.J., et al. Targeted disruption of the glucose transporter 4 selectively in muscle causes insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. Nat. Med. 2000;6:924–928. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

